Poly (Lactic- co-Glycolic Acid) Nanoparticles and Nanoliposomes for Protein Delivery in Targeted Therapy: A Comparative In Vitro Study
- PMID: 33139610
- PMCID: PMC7692461
- DOI: 10.3390/polym12112566
Poly (Lactic- co-Glycolic Acid) Nanoparticles and Nanoliposomes for Protein Delivery in Targeted Therapy: A Comparative In Vitro Study
Abstract
Over the previous years, the design, development, and potential application of nanocarriers in the medical field have been intensively studied for their ability to preserve drug properties, especially their pharmacological activity, and to improve their bioavailability. This work is a comparative study between two different types of nanocarriers, poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid)-based nanoparticles and phosphatidylcholine-based nanoliposomes, both prepared for the encapsulation of bovine serum albumin as a model protein. Polymeric nanoparticles were produced using the double emulsion water-oil-water evaporation method, whereas nanoliposomes were obtained by the thin-film hydration method. Both nanocarriers were characterized by morphological analysis, particle mean size, particle size distribution, and protein entrapment efficiency. Invitro release studies were performed for 12 days at 37 °C. In order to explore a possible application of these nanocarriers for a targeted therapy in the cardiovascular field, hemolytic activity and biocompatibility, in terms of cell viability, were performed by using human red blood cells and EA.hy926 human endothelial cell line, respectively.
Keywords: biocompatibility; cardiovascular diseases; hemolysis; lipid-based nanosystem; nanocarriers; phosphatidylcholine; poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid); polymer-based nanosystem; protein drug delivery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
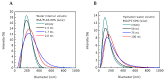
 PNPBSA (30 mg/mL),
PNPBSA (30 mg/mL),  PNPBSA (35 mg/mL),
PNPBSA (35 mg/mL),  PNPBSA (40 mg/mL) and from (B) NLPs:
PNPBSA (40 mg/mL) and from (B) NLPs:  NLPBSA (3 mg/mL),
NLPBSA (3 mg/mL),  NLPBSA (4 mg/mL),
NLPBSA (4 mg/mL),  NLPBSA (6 mg/mL). Data are expressed as mean of three measurements. Error bars indicate SD. BSA: bovine serum albumin, PNPs: polymeric nanoparticles, NLPs: nanoliposomes.
NLPBSA (6 mg/mL). Data are expressed as mean of three measurements. Error bars indicate SD. BSA: bovine serum albumin, PNPs: polymeric nanoparticles, NLPs: nanoliposomes.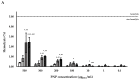
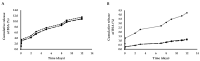
 PNPE,
PNPE,  PNPBSA (30 mg/mL),
PNPBSA (30 mg/mL),  PNPBSA (35 mg/mL),
PNPBSA (35 mg/mL),  PNPBSA (40 mg/mL) and of (B) NLPs:
PNPBSA (40 mg/mL) and of (B) NLPs:  NLPE,
NLPE,  NLPBSA (3 mg/mL),
NLPBSA (3 mg/mL),  NLPBSA (4 mg/mL),
NLPBSA (4 mg/mL),  NLPBSA (6 mg/mL). RBCs: red blood cells, PNPE: empty polymeric nanoparticles, PNPBSA: BSA-loaded polymeric nanoparticles, NLPE: empty nanoliposomes, NLPBSA: BSA-loaded nanoliposomes. Data are expressed as mean of three measurements. Error bars indicate SD. Different symbols refer to statistically significant differences among results (p < 0.05, ANOVA with Tukey’s HSD post hoc multiple comparison test). a: statistically different to empty nanocarriers (PNPE or NLPE), aa: statistically different to PNPBSA (30 mg/mL) or NLPBSA (3 mg/mL), aaa: statistically different to PNPBSA (35 mg/mL) or NLPBSA (4 mg/mL). The dotted line refers to 5% of hemolysis.
NLPBSA (6 mg/mL). RBCs: red blood cells, PNPE: empty polymeric nanoparticles, PNPBSA: BSA-loaded polymeric nanoparticles, NLPE: empty nanoliposomes, NLPBSA: BSA-loaded nanoliposomes. Data are expressed as mean of three measurements. Error bars indicate SD. Different symbols refer to statistically significant differences among results (p < 0.05, ANOVA with Tukey’s HSD post hoc multiple comparison test). a: statistically different to empty nanocarriers (PNPE or NLPE), aa: statistically different to PNPBSA (30 mg/mL) or NLPBSA (3 mg/mL), aaa: statistically different to PNPBSA (35 mg/mL) or NLPBSA (4 mg/mL). The dotted line refers to 5% of hemolysis.
 PNPE,
PNPE,  PNPBSA (30 mg/mL),
PNPBSA (30 mg/mL),  PNPBSA (35 mg/mL),
PNPBSA (35 mg/mL),  PNPBSA (40 mg/mL) and of (B) NLPs:
PNPBSA (40 mg/mL) and of (B) NLPs:  NLPE,
NLPE,  NLPBSA (3 mg/mL),
NLPBSA (3 mg/mL),  NLPBSA (4 mg/mL),
NLPBSA (4 mg/mL),  NLPBSA (6 mg/mL). RBCs: red blood cells, PNPE: empty polymeric nanoparticles, PNPBSA: BSA-loaded polymeric nanoparticles, NLPE: empty nanoliposomes, NLPBSA: BSA-loaded nanoliposomes. Data are expressed as mean of three measurements. Error bars indicate SD. Different symbols refer to statistically significant differences among results (p < 0.05, ANOVA with Tukey’s HSD post hoc multiple comparison test). a: statistically different to empty nanocarriers (PNPE or NLPE), aa: statistically different to PNPBSA (30 mg/mL) or NLPBSA (3 mg/mL), aaa: statistically different to PNPBSA (35 mg/mL) or NLPBSA (4 mg/mL). The dotted line refers to 5% of hemolysis.
NLPBSA (6 mg/mL). RBCs: red blood cells, PNPE: empty polymeric nanoparticles, PNPBSA: BSA-loaded polymeric nanoparticles, NLPE: empty nanoliposomes, NLPBSA: BSA-loaded nanoliposomes. Data are expressed as mean of three measurements. Error bars indicate SD. Different symbols refer to statistically significant differences among results (p < 0.05, ANOVA with Tukey’s HSD post hoc multiple comparison test). a: statistically different to empty nanocarriers (PNPE or NLPE), aa: statistically different to PNPBSA (30 mg/mL) or NLPBSA (3 mg/mL), aaa: statistically different to PNPBSA (35 mg/mL) or NLPBSA (4 mg/mL). The dotted line refers to 5% of hemolysis.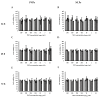
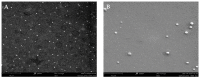
 control (without particles),
control (without particles),  PNPE (A,C,E),
PNPE (A,C,E),  PNPBSA (40mg/mL) (A,C,E),
PNPBSA (40mg/mL) (A,C,E),  NLPE (B,D,F),
NLPE (B,D,F),  NLPBSA (3 mg/mL) (B,D,F). PNPE: empty polymeric nanoparticles, PNPBSA: BSA-loaded polymeric nanoparticles, NLPE: empty nanoliposomes, NLPBSA: BSA-loaded nanoliposomes. Data are expressed as mean of three measurements. Error bars indicate SD. Different symbols refer to statistically significant differences among results (p < 0.05, ANOVA with Tukey’s HSD post hoc multiple comparison test). a: statistically different to control, aa: statistically different to empty carrier.
NLPBSA (3 mg/mL) (B,D,F). PNPE: empty polymeric nanoparticles, PNPBSA: BSA-loaded polymeric nanoparticles, NLPE: empty nanoliposomes, NLPBSA: BSA-loaded nanoliposomes. Data are expressed as mean of three measurements. Error bars indicate SD. Different symbols refer to statistically significant differences among results (p < 0.05, ANOVA with Tukey’s HSD post hoc multiple comparison test). a: statistically different to control, aa: statistically different to empty carrier.Similar articles
-
Bevacizumab-Controlled Delivery from Polymeric Microparticle Systems as Interesting Tools for Pathologic Angiogenesis Diseases.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Jun 26;14(13):2593. doi: 10.3390/polym14132593. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35808639 Free PMC article.
-
Co-association of methotrexate and SPIONs into anti-CD64 antibody-conjugated PLGA nanoparticles for theranostic application.Int J Nanomedicine. 2014 Oct 23;9:4911-22. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S68440. eCollection 2014. Int J Nanomedicine. 2014. PMID: 25364249 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative study of superparamagnetic iron oxide/doxorubicin co-loaded poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanospheres prepared by different emulsion solvent evaporation methods.Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2018 Sep;46(6):1146-1155. doi: 10.1080/21691401.2017.1362415. Epub 2017 Aug 9. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 28789586
-
Lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles as a new generation therapeutic delivery platform: a review.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2013 Nov;85(3 Pt A):427-43. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2013.07.002. Epub 2013 Jul 17. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2013. PMID: 23872180 Review.
-
Polymer-based nanoparticles for oral insulin delivery: Revisited approaches.Biotechnol Adv. 2015 Nov 1;33(6 Pt 3):1342-54. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2015.02.010. Epub 2015 Feb 26. Biotechnol Adv. 2015. PMID: 25728065 Review.
Cited by
-
Ocular Delivery of Therapeutic Proteins: A Review.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jan 6;15(1):205. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15010205. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36678834 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Genoa Vascular Biobank: A Today Resource for Future Perspectives in Vascular Research.Biomark Insights. 2025 Jul 13;20:11772719251324322. doi: 10.1177/11772719251324322. eCollection 2025. Biomark Insights. 2025. PMID: 40661258 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in RNAi-based nanoformulations: revolutionizing crop protection and stress tolerance in agriculture.Nanoscale Adv. 2025 Mar 4;7(7):1768-1783. doi: 10.1039/d5na00044k. eCollection 2025 Mar 25. Nanoscale Adv. 2025. PMID: 40046252 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TB@PLGA Nanoparticles for Photodynamic/Photothermal Combined Cancer Therapy with Single Near-Infrared Irradiation.Int J Nanomedicine. 2021 Jul 16;16:4863-4871. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S304713. eCollection 2021. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021. PMID: 34295159 Free PMC article.
-
Maltodextrin-Nanoparticles as a Delivery System for Nasal Vaccines: A Review Article.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Feb 7;16(2):247. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16020247. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 38399301 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

