Nutrition Management in Older Adults with Diabetes: A Review on the Importance of Shifting Prevention Strategies from Metabolic Syndrome to Frailty
- PMID: 33139628
- PMCID: PMC7693664
- DOI: 10.3390/nu12113367
Nutrition Management in Older Adults with Diabetes: A Review on the Importance of Shifting Prevention Strategies from Metabolic Syndrome to Frailty
Abstract
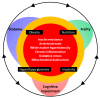
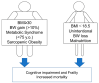
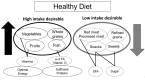
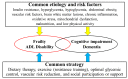
The increasing prevalence of older adults with diabetes has become a major social burden. Diabetes, frailty, and cognitive dysfunction are closely related to the mechanisms of aging. Insulin resistance, arteriosclerosis, chronic inflammation, oxidative stress, and mitochondrial dysfunction may be common mechanisms shared by frailty and cognitive impairment. Hyperglycemia, hypoglycemia, obesity, vascular factors, physical inactivity, and malnutrition are important risk factors for cognitive impairment and frailty in older adults with diabetes. The impact of nutrients on health outcomes varies with age; thus, shifting diet therapy strategies from the treatment of obesity/metabolic syndrome to frailty prevention may be necessary in patients with diabetes who are over 75 years of age, have frailty or sarcopenia, and experience malnutrition. For the prevention of frailty, optimal energy intake, sufficient protein and vitamin intake, and healthy dietary patterns should be recommended. The treatment of diabetes after middle age should include the awareness of proper glycemic control aimed at extending healthy life expectancy with proper nutrition, exercise, and social connectivity. Nutritional therapy in combination with exercise, optimal glycemic and metabolic control, and social participation/support for frailty prevention can extend healthy life expectancy and maintain quality of life in older adults with diabetes mellitus.
Keywords: cognitive impairment; diabetes mellitus; elderly; frailty; nutrition management.
Conflict of interest statement
Araki A has received speaker honoraria from pharmaceutical companies, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Dainippon Sumitomo Parma Co. Ltd., Kyowa Hakko Kirin Co. Ltd., Tanabe Mitsubishi Pharma Corporation, Takeda Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Malnutrition and sarcopenia.Aging Clin Exp Res. 2019 Jun;31(6):793-798. doi: 10.1007/s40520-019-01170-1. Epub 2019 May 30. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2019. PMID: 31148100 Review.
-
Empowering Pre-Frail Older Adults: Assessing the Effects of a Community Nutrition Education Intervention on Nutritional Intake and Sarcopenia Markers.Nutrients. 2025 Apr 30;17(9):1531. doi: 10.3390/nu17091531. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40362841 Free PMC article.
-
Skeletal muscle as a treatment target for older adults with diabetes mellitus: The importance of a multimodal intervention based on functional category.Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2022 Feb;22(2):110-120. doi: 10.1111/ggi.14339. Epub 2022 Jan 5. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2022. PMID: 34986525 Review.
-
Sarcopenia, frailty and their prevention by exercise.Free Radic Biol Med. 2019 Feb 20;132:42-49. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.08.035. Epub 2018 Aug 31. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019. PMID: 30176345 Review.
-
The role of nutrition and physical activity in frailty: A review.Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2020 Feb;35:1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.clnesp.2019.11.003. Epub 2019 Dec 6. Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2020. PMID: 31987100 Review.
Cited by
-
Prevalence and predictors of hypoglycemia in older outpatients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.PLoS One. 2024 Aug 29;19(8):e0309618. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0309618. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39208059 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of three clinical nutrition scoring system (NRI, PNI, and CONUT) in elderly patients with prostate cancer.Front Nutr. 2024 Oct 1;11:1436063. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1436063. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39410925 Free PMC article.
-
Combined effect of diabetes and frailty on mortality among Chinese older adults: A follow-up study.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Jan 16;13:1105957. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1105957. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36726468 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and its association with age in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.World J Hepatol. 2022 Jun 27;14(6):1226-1234. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v14.i6.1226. World J Hepatol. 2022. PMID: 35978658 Free PMC article.
-
SGLT2 Inhibition via Empagliflozin Improves Endothelial Function and Reduces Mitochondrial Oxidative Stress: Insights From Frail Hypertensive and Diabetic Patients.Hypertension. 2022 Aug;79(8):1633-1643. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.122.19586. Epub 2022 Jun 15. Hypertension. 2022. PMID: 35703100 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pensions at a Glance 2019: OECD and G20 Indicators. OECD Publishing; Paris, France: 2019.
-
- Charvat H., Goto A., Goto M., Inoue M., Heianza Y., Arase Y., Sone H., Nakagami T., Song X., Qiao Q., et al. Impact of population aging on trends in diabetes prevalence: A meta-regression analysis of 160,000 Japanese adults. J. Diabetes Investig. 2015;6:533–542. doi: 10.1111/jdi.12333. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

