Role of Inositols and Inositol Phosphates in Energy Metabolism
- PMID: 33139672
- PMCID: PMC7663797
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25215079
Role of Inositols and Inositol Phosphates in Energy Metabolism
Abstract
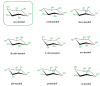
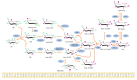
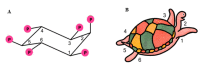
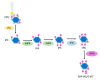
Recently, inositols, especially myo-inositol and inositol hexakisphosphate, also known as phytic acid or IP6, with their biological activities received much attention for their role in multiple health beneficial effects. Although their roles in cancer treatment and prevention have been extensively reported, interestingly, they may also have distinctive properties in energy metabolism and metabolic disorders. We review inositols and inositol phosphate metabolism in mammalian cells to establish their biological activities and highlight their potential roles in energy metabolism. These molecules are known to decrease insulin resistance, increase insulin sensitivity, and have diverse properties with importance from cell signaling to metabolism. Evidence showed that inositol phosphates might enhance the browning of white adipocytes and directly improve insulin sensitivity through adipocytes. In addition, inositol pyrophosphates containing high-energy phosphate bonds are considered in increasing cellular energetics. Despite all recent advances, many aspects of the bioactivity of inositol phosphates are still not clear, especially their effects on insulin resistance and alteration of metabolism, so more research is needed.
Keywords: IP6; energy metabolism; inositol phosphates; insulin resistance; myo-inositol.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this manuscript and we have no financial interests in any commercial sources of inositol, IP6 or other inositol phosphates.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inositol pyrophosphates: between signalling and metabolism.Biochem J. 2013 Jun 15;452(3):369-79. doi: 10.1042/BJ20130118. Biochem J. 2013. PMID: 23725456 Review.
-
Inositol Pyrophosphates as Versatile Metabolic Messengers.Annu Rev Biochem. 2024 Aug;93(1):317-338. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-030222-121901. Annu Rev Biochem. 2024. PMID: 39094034 Review.
-
Inositol Pyrophosphates: Signaling Molecules with Pleiotropic Actions in Mammals.Molecules. 2020 May 8;25(9):2208. doi: 10.3390/molecules25092208. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32397291 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phytic acid and myo-inositol support adipocyte differentiation and improve insulin sensitivity in 3T3-L1 cells.Nutr Res. 2014 Aug;34(8):723-31. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2014.07.015. Epub 2014 Jul 30. Nutr Res. 2014. PMID: 25174657
-
Potential role and therapeutic interests of myo-inositol in metabolic diseases.Biochimie. 2013 Oct;95(10):1811-27. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2013.05.011. Epub 2013 Jun 10. Biochimie. 2013. PMID: 23764390 Review.
Cited by
-
Insulin-Heart Axis: Bridging Physiology to Insulin Resistance.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 31;25(15):8369. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158369. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39125938 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Maturation and culture affect the metabolomic profile of oocytes and follicular cells in young and old mares.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Jan 12;11:1280998. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1280998. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 38283993 Free PMC article.
-
Harnessing the Power of Purple Sweet Potato Color and Myo-Inositol to Treat Classic Galactosemia.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 4;23(15):8654. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158654. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35955788 Free PMC article.
-
An In Vivo CRISPR Screening Platform for Prioritizing Therapeutic Targets in AML.Cancer Discov. 2022 Feb;12(2):432-449. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-20-1851. Epub 2021 Sep 16. Cancer Discov. 2022. PMID: 34531254 Free PMC article.
-
Myo-Inositol Supplementation Alleviates Cisplatin-Induced Acute Kidney Injury via Inhibition of Ferroptosis.Cells. 2022 Dec 21;12(1):16. doi: 10.3390/cells12010016. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36611810 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shamsuddin A.K., Bose S. IP6 (Inositol Hexaphosphate) as a Signaling Molecule. Curr. Cancer Rev. 2012;7:289–304. doi: 10.2174/157436212802481628. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

