Phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase signalling is spatially organized at endosomal compartments by microtubule-associated protein 4
- PMID: 33139939
- PMCID: PMC8647654
- DOI: 10.1038/s41556-020-00596-4
Phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase signalling is spatially organized at endosomal compartments by microtubule-associated protein 4
Abstract
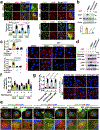
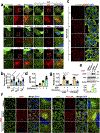
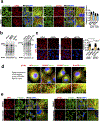
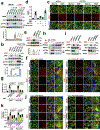
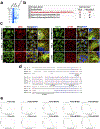
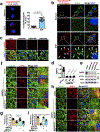
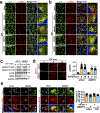
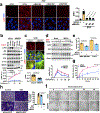
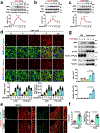
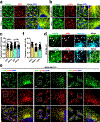
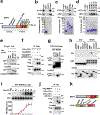
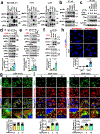
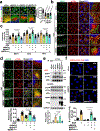
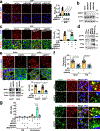
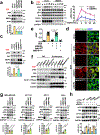
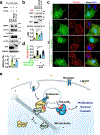
The canonical model of agonist-stimulated phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase (PI3K)-Akt signalling proposes that PI3K is activated at the plasma membrane, where receptors are activated and phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate is concentrated. Here we show that phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate generation and activated Akt are instead largely confined to intracellular membranes upon receptor tyrosine kinase activation. Microtubule-associated protein 4 (MAP4) interacts with and controls localization of membrane vesicle-associated PI3Kα to microtubules. The microtubule-binding domain of MAP4 binds directly to the C2 domain of the p110α catalytic subunit. MAP4 controls the interaction of PI3Kα with activated receptors at endosomal compartments along microtubules. Loss of MAP4 results in the loss of PI3Kα targeting and loss of PI3K-Akt signalling downstream of multiple agonists. The MAP4-PI3Kα assembly defines a mechanism for spatial control of agonist-stimulated PI3K-Akt signalling at internal membrane compartments linked to the microtubule network.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare no competing interests
Figures
Comment in
-
A MAP for PI3K activation on endosomes.Nat Cell Biol. 2020 Nov;22(11):1292-1294. doi: 10.1038/s41556-020-00597-3. Nat Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 33139938 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
A p85 isoform switch enhances PI3K activation on endosomes by a MAP4- and PI3P-dependent mechanism.Cell Rep. 2024 May 28;43(5):114119. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114119. Epub 2024 Apr 16. Cell Rep. 2024. PMID: 38630589 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of activation of SGK3 by growth factors via the Class 1 and Class 3 PI3Ks.Biochem J. 2018 Jan 2;475(1):117-135. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20170650. Biochem J. 2018. PMID: 29150437 Free PMC article.
-
The type Ialpha inositol polyphosphate 4-phosphatase generates and terminates phosphoinositide 3-kinase signals on endosomes and the plasma membrane.Mol Biol Cell. 2005 May;16(5):2218-33. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e04-09-0799. Epub 2005 Feb 16. Mol Biol Cell. 2005. PMID: 15716355 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of PI3K effector signalling in cancer by the phosphoinositide phosphatases.Biosci Rep. 2017 Feb 10;37(1):BSR20160432. doi: 10.1042/BSR20160432. Print 2017 Feb 28. Biosci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28082369 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate: tool of choice for class I PI 3-kinases.Bioessays. 2013 Jul;35(7):602-11. doi: 10.1002/bies.201200176. Bioessays. 2013. PMID: 23765576 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of EGF-stimulated activation of the PI-3K/AKT pathway by exocyst-mediated exocytosis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Nov 29;119(48):e2208947119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2208947119. Epub 2022 Nov 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 36417441 Free PMC article.
-
IQGAP1 scaffolding links phosphoinositide kinases to cytoskeletal reorganization.Biophys J. 2022 Mar 1;121(5):793-807. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2022.01.018. Epub 2022 Jan 22. Biophys J. 2022. PMID: 35077666 Free PMC article.
-
Asparagine endopeptidase regulates lysosome homeostasis via modulating endomembrane phosphoinositide composition.Cell Death Dis. 2025 Jan 2;15(12):883. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-07187-3. Cell Death Dis. 2025. PMID: 39743643 Free PMC article.
-
CHKB-AS1 enhances proliferation and resistance to NVP-BEZ235 of renal cancer cells via regulating the phosphorylation of MAP4 and PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling.Eur J Med Res. 2023 Dec 14;28(1):588. doi: 10.1186/s40001-023-01558-w. Eur J Med Res. 2023. PMID: 38093375 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Cell Adhesion and Migration via Microtubule Cytoskeleton Organization, Cell Polarity, and Phosphoinositide Signaling.Biomolecules. 2023 Sep 22;13(10):1430. doi: 10.3390/biom13101430. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37892112 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

