Asphericity of tumor FDG uptake in non-small cell lung cancer: reproducibility and implications for harmonization in multicenter studies
- PMID: 33140213
- PMCID: PMC7606415
- DOI: 10.1186/s13550-020-00725-y
Asphericity of tumor FDG uptake in non-small cell lung cancer: reproducibility and implications for harmonization in multicenter studies
Abstract
Background: Asphericity (ASP) of the primary tumor's metabolic tumor volume (MTV) in FDG-PET/CT is independently predictive for survival in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). However, comparability between PET systems may be limited. Therefore, reproducibility of ASP was evaluated at varying image reconstruction and acquisition times to assess feasibility of ASP assessment in multicenter studies.
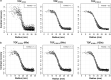
Methods: This is a retrospective study of 50 patients with NSCLC (female 20; median age 69 years) undergoing pretherapeutic FDG-PET/CT (median 3.7 MBq/kg; 180 s/bed position). Reconstruction used OSEM with TOF4/16 (iterations 4; subsets 16; in-plane filter 2.0, 6.4 or 9.5 mm), TOF4/8 (4 it; 8 ss; filter 2.0/6.0/9.5 mm), PSF + TOF2/17 (2 it; 17 ss; filter 2.0/7.0/10.0 mm) or Bayesian-penalized likelihood (Q.Clear; beta, 600/1750/4000). Resulting reconstructed spatial resolution (FWHM) was determined from hot sphere inserts of a NEMA IEC phantom. Data with approx. 5-mm FWHM were retrospectively smoothed to achieve 7-mm FWHM. List mode data were rebinned for acquisition times of 120/90/60 s. Threshold-based delineation of primary tumor MTV was followed by evaluation of relative ASP/SUVmax/MTV differences between datasets and resulting proportions of discordantly classified cases.
Results: Reconstructed resolution for narrow/medium/wide in-plane filter (or low/medium/high beta) was approx. 5/7/9 mm FWHM. Comparing different pairs of reconstructed resolution between TOF4/8, PSF + TOF2/17, Q.Clear and the reference algorithm TOF4/16, ASP differences was lowest at FWHM of 7 versus 7 mm. Proportions of discordant cases (ASP > 19.5% vs. ≤ 19.5%) were also lowest at 7 mm (TOF4/8, 2%; PSF + TOF2/17, 4%; Q.Clear, 10%). Smoothing of 5-mm data to 7-mm FWHM significantly reduced discordant cases (TOF4/8, 38% reduced to 2%; PSF + TOF2/17, 12% to 4%; Q.Clear, 10% to 6%), resulting in proportions comparable to original 7-mm data. Shorter acquisition time only increased proportions of discordant cases at < 90 s.
Conclusions: ASP differences were mainly determined by reconstructed spatial resolution, and multicenter studies should aim at comparable FWHM (e.g., 7 mm; determined by in-plane filter width). This reduces discordant cases (high vs. low ASP) to an acceptable proportion for TOF and PSF + TOF of < 5% (Q.Clear: 10%). Data with better resolution (i.e., lower FWHM) could be retrospectively smoothed to the desired FWHM, resulting in a comparable number of discordant cases.
Keywords: Asphericity; FDG-PET; Image reconstruction; Non-small cell lung cancer; Prognosis; Reproducibility; Spatial resolution.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Reconstructed spatial resolution and contrast recovery with Bayesian penalized likelihood reconstruction (Q.Clear) for FDG-PET compared to time-of-flight (TOF) with point spread function (PSF).EJNMMI Phys. 2020 Jan 10;7(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s40658-020-0270-y. EJNMMI Phys. 2020. PMID: 31925574 Free PMC article.
-
The influence of different signal-to-background ratios on spatial resolution and F18-FDG-PET quantification using point spread function and time-of-flight reconstruction.EJNMMI Phys. 2014 Dec;1(1):12. doi: 10.1186/2197-7364-1-12. Epub 2014 Sep 19. EJNMMI Phys. 2014. PMID: 26501454 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization of a Bayesian penalized likelihood algorithm (Q.Clear) for 18F-NaF bone PET/CT images acquired over shorter durations using a custom-designed phantom.EJNMMI Phys. 2020 Sep 11;7(1):56. doi: 10.1186/s40658-020-00325-8. EJNMMI Phys. 2020. PMID: 32915344 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of a Bayesian penalized likelihood reconstruction algorithm for low-count clinical 18F-FDG PET/CT.EJNMMI Phys. 2019 Dec 30;6(1):32. doi: 10.1186/s40658-019-0262-y. EJNMMI Phys. 2019. PMID: 31889228 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative assessment of the asphericity of pretherapeutic FDG uptake as an independent predictor of outcome in NSCLC.BMC Cancer. 2014 Dec 1;14:896. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-896. BMC Cancer. 2014. PMID: 25444154 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Combination of tumor asphericity and an extracellular matrix-related prognostic gene signature in non-small cell lung cancer patients.Sci Rep. 2023 Nov 27;13(1):20840. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-46405-4. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 38012155 Free PMC article.
-
A machine learning tool to improve prediction of mediastinal lymph node metastases in non-small cell lung cancer using routinely obtainable [18F]FDG-PET/CT parameters.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2023 Jun;50(7):2140-2151. doi: 10.1007/s00259-023-06145-z. Epub 2023 Feb 23. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2023. PMID: 36820890 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor Asphericity in FDG PET Is an Independent Prognostic Parameter Improving Risk Stratification in Patients with Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma.J Nucl Med. 2025 May 1;66(5):686-691. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.124.268972. J Nucl Med. 2025. PMID: 40081960
References
-
- Douillard JY, Rosell R, De Lena M, Carpagnano F, Ramlau R, Gonzales-Larriba JL, et al. Adjuvant vinorelbine plus cisplatin versus observation in patients with completely resected stage IB-IIIA non-small-cell lung cancer (Adjuvant Navelbine International Trialist Association [ANITA]): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2006;7(9):719–727. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(06)70804-X. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

