Incremental Predictive Value of Plasma Renin Activity as a Prognostic Biomarker in Patients with Heart Failure
- PMID: 33140588
- PMCID: PMC7606887
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e351
Incremental Predictive Value of Plasma Renin Activity as a Prognostic Biomarker in Patients with Heart Failure
Abstract
Background: The association of N-terminal pro-B type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) and plasma renin activity (PRA) for the prognosis of the patients with acute heart failure (HF) has not been fully investigated. This study aimed to determine the association between NT-proBNP and PRA and to investigate the incremental value of PRA to NT-proBNP for predicting long term prognosis in patients with acute HF.
Methods: Three hundred and ninety-six patients (mean age, 64.7 ± 15.9 years; 46.5% female) presenting with acute HF were enrolled between December 2004 and July 2013. Patients with newly diagnosed HF as well as patients with acute exacerbated chronic HF were included. The prognosis was assessed with the composite event of all-cause mortality and readmission for HF during a 2-year follow-up period.
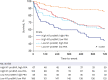
Results: The etiology of HF was ischemic in 116 (29.3%) patients. In a Cox proportional hazards model, log-transformed PRA (hazard ratio [HR], 1.205; P = 0.007) was an independent predictor of the composite outcome of all-cause mortality and readmission for HF in addition to age (HR, 1.032; P = 0.001), white blood cell (WBC) count (HR, 1.103; P < 0.001), and left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) (HR, 0.978; P = 0.013). Adding PRA to age, sex, LVEF, and NT-proBNP significantly improved the prediction for the composite outcome of all-cause mortality and readmission for HF, as shown by the net reclassification improvement (0.47; P < 0.001) and integrated discrimination improvement (0.10; P < 0.001).
Conclusion: PRA could provide incremental predictive value to NT-proBNP for predicting long term prognosis in patients with acute HF.
Keywords: Heart Failure; Natriuretic Peptides; Prognosis; Renin.
© 2020 The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prognostic value of plasma renin activity in heart failure patients with chronic kidney disease.Int J Cardiol. 2013 Aug 10;167(3):711-5. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2012.03.061. Epub 2012 Mar 28. Int J Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 22459392
-
Prognostic value of plasma renin activity in heart failure.Am J Cardiol. 2011 Jul 15;108(2):246-51. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2011.03.034. Epub 2011 May 3. Am J Cardiol. 2011. PMID: 21545993
-
The Additional Prognostic Value of Ghrelin for Mortality and Readmission in Elderly Patients with Acute Heart Failure.Clin Interv Aging. 2020 Aug 11;15:1353-1363. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S259889. eCollection 2020. Clin Interv Aging. 2020. PMID: 32848376 Free PMC article.
-
The predictive value of plasma biomarkers in discharged heart failure patients: role of plasma NT-proBNP.Minerva Cardioangiol. 2016 Apr;64(2):157-64. Epub 2015 Sep 15. Minerva Cardioangiol. 2016. PMID: 26373781 Review.
-
Potential of plasma biomarkers for heart failure prediction, management, and prognosis: A multiomics perspective.Heart Fail Rev. 2025 Jan;30(1):55-67. doi: 10.1007/s10741-024-10443-5. Epub 2024 Oct 8. Heart Fail Rev. 2025. PMID: 39377997 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluating Biomarkers as Tools for Early Detection and Prognosis of Heart Failure: A Comprehensive Review.Card Fail Rev. 2024 Jun 3;10:e06. doi: 10.15420/cfr.2023.24. eCollection 2024. Card Fail Rev. 2024. PMID: 38915376 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Emdin M, Vittorini S, Passino C, Clerico A. Old and new biomarkers of heart failure. Eur J Heart Fail. 2009;11(4):331–335. - PubMed
-
- Khanam SS, Choi E, Son JW, Lee JW, Youn YJ, Yoon J, et al. Validation of the MAGGIC (Meta-Analysis Global Group in Chronic Heart Failure) heart failure risk score and the effect of adding natriuretic peptide for predicting mortality after discharge in hospitalized patients with heart failure. PLoS One. 2018;13(11):e0206380. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Braunwald E. Biomarkers in heart failure. N Engl J Med. 2008;358(20):2148–2159. - PubMed
-
- Schmieder RE, Hilgers KF, Schlaich MP, Schmidt BM. Renin-angiotensin system and cardiovascular risk. Lancet. 2007;369(9568):1208–1219. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

