Predictors of in-hospital COVID-19 mortality: A comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis exploring differences by age, sex and health conditions
- PMID: 33141836
- PMCID: PMC7608886
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0241742
Predictors of in-hospital COVID-19 mortality: A comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis exploring differences by age, sex and health conditions
Abstract
Objective: Risk factors for in-hospital mortality in confirmed COVID-19 patients have been summarized in numerous meta-analyses, but it is still unclear whether they vary according to the age, sex and health conditions of the studied populations. This study explored these variables as potential mortality predictors.
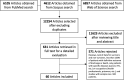
Methods: A systematic review was conducted by searching the MEDLINE, Scopus, and Web of Science databases of studies available through July 27, 2020. The pooled risk was estimated with the odds ratio (p-OR) or effect size (p-ES) obtained through random-effects meta-analyses. Subgroup analyses and meta-regression were applied to explore differences by age, sex and health conditions. The MOOSE guidelines were strictly followed.
Results: The meta-analysis included 60 studies, with a total of 51,225 patients (12,458 [24.3%] deaths) from hospitals in 13 countries. A higher in-hospital mortality risk was found for dyspnoea (p-OR = 2.5), smoking (p-OR = 1.6) and several comorbidities (p-OR range: 1.8 to 4.7) and laboratory parameters (p-ES range: 0.3 to -2.6). Age was the main source of heterogeneity, followed by sex and health condition. The following predictors were more markedly associated with mortality in studies with patients with a mean age ≤60 years: dyspnoea (p-OR = 4.3), smoking (p-OR = 2.8), kidney disease (p-OR = 3.8), hypertension (p-OR = 3.7), malignancy (p-OR = 3.7), diabetes (p-OR = 3.2), pulmonary disease (p-OR = 3.1), decreased platelet count (p-ES = -1.7), decreased haemoglobin concentration (p-ES = -0.6), increased creatinine (p-ES = 2.4), increased interleukin-6 (p-ES = 2.4) and increased cardiac troponin I (p-ES = 0.7). On the other hand, in addition to comorbidities, the most important mortality predictors in studies with older patients were albumin (p-ES = -3.1), total bilirubin (p-ES = 0.7), AST (p-ES = 1.8), ALT (p-ES = 0.4), urea nitrogen (p-ES), C-reactive protein (p-ES = 2.7), LDH (p-ES = 2.4) and ferritin (p-ES = 1.7). Obesity was associated with increased mortality only in studies with fewer chronic or critical patients (p-OR = 1.8).
Conclusion: The prognostic effect of clinical conditions on COVID-19 mortality vary substantially according to the mean age of patients.
Prospero registration number: CRD42020176595.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization W. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Situation Report– 72. 2020.
-
- Grant MC, Geoghegan L, Arbyn M, Mohammed Z, McGuinness L, Clarke EL, et al. The prevalence of symptoms in 24,410 adults infected by the novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2; COVID-19): A systematic review and meta-analysis of 148 studies from 9 countries. PLoS One. 2020;15:e0234765 Epub 2020/06/24. 10.1371/journal.pone.0234765 eCollection 2020. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Karlsen APH, Wiberg S, Laigaard J, Pedersen C, Rokamp KZ, Mathiesen O. A systematic review of trial registry entries for randomized clinical trials investigating COVID-19 medical prevention and treatment. PLoS One. 2020;15(8):e0237903 Epub 2020/08/21. 10.1371/journal.pone.0237903 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials