Immediate placement of single implants with or without immediate provisionalization in the maxillary aesthetic region: A 5-year comparative study
- PMID: 33141935
- PMCID: PMC7839711
- DOI: 10.1111/jcpe.13398
Immediate placement of single implants with or without immediate provisionalization in the maxillary aesthetic region: A 5-year comparative study
Abstract
Aim: To compare marginal bone level changes around immediately placed and immediately provisionalized implants with immediately placed and delayed provisionalized implants in the aesthetic region after five years of function.
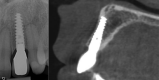
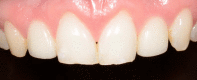
Materials and methods: Forty patients with a failing tooth in the maxillary anterior region were randomly assigned immediate implant placement with immediate (Group A: n = 20) or delayed (Group B: n = 20) provisionalization. Definitive crown placement occurred three months after provisionalization. The primary outcomes were changes in marginal bone level. In addition, survival rates, buccal bone thickness, soft peri-implant tissues, aesthetics and patient-reported outcomes were assessed.
Results: After 5 years, the mean mesial and distal marginal bone level changes were 0.71 ± 0.68 mm and 0.71 ± 0.71 mm, respectively, in group A and 0.49 ± 0.52 mm and 0.54 ± 0.64 mm, respectively, in group B; the difference between the groups was not significant (p = .305 and p = .477, respectively). Implant and restoration survivals were 100%. No clinically relevant differences in buccal bone thickness or in mid-facial peri-implant mucosal level, aesthetic and patient outcomes were observed.
Conclusions: The mean marginal bone level changes following immediate implant placement and provisionalization were comparable with immediate implant placement and delayed provisionalization. (www.isrctn.com: ISRCTN57251089 and www.trialregister.nl: NL8255).
Keywords: aesthetic region; dental implants; immediate placement.
© 2020 The Authors. Journal of Clinical Periodontology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Belser, U. C. , Grutter, L. , Vailati, F. , Bornstein, M. M. , Weber, H. P. , & Buser, D. (2009). Outcome evaluation of early placed maxillary anterior single‐tooth implants using objective esthetic criteria: A cross‐sectional, retrospective study in 45 patients with a 2‐ to 4‐year follow‐up using pink and white esthetic scores. Journal of Periodontology, 80(1), 140–151. 10.1902/jop.2009.080435 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Berglundh, T. , Armitage, G. , Araujo, M. G. , Avila‐Ortiz, G. , Blanco, J. , Camargo, P. M. , Chen, S. , Cochran, D. , Derks, J. , Figuero, E. , Hämmerle, C. H. F. , Heitz‐Mayfield, L. J. A. , Huynh‐Ba, G. , Iacono, V. , Koo, K. T. , Lambert, F. , McCauley, L. , Quirynen, M. , Renvert, S. , Salvi, G. E. , & Zitzmann, N. (2018). Peri‐implant diseases and conditions: Consensus report of workgroup 4 of the 2017 World Workshop on the Classification of Periodontal and Peri‐Implant Diseases and Conditions. Journal of Clinical Periodontology, 45(Suppl 20), S286–S291. 10.1111/jcpe.12957 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Canellas, J. V. D. S. , Medeiros, P. J. D. , Figueredo, C. M. D. S. , Fischer, R. G. , & Ritto, F. G. (2019). Which is the best choice after tooth extraction, immediate implant placement or delayed placement with alveolar ridge preservation? A systematic review and meta‐analysis. Journal of Craniomaxillofacial Surgery, 47(11), 1793–1802. 10.1016/j.jcms.2019.08.004 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cooper, L. F. , Reside, G. , Raes, F. , Garriga, J. S. , Tarrida, L. G. , Wiltfang, J. , Kern, M. , & De Bruyn, H. (2014a). Immediate provisionalization of dental implants in grafted alveolar ridges in the esthetic zone: A 5‐year evaluation. International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry, 34(4), 477–486. 10.11607/prd.2022 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

