In vitro effects of 5 recombinant antigens of Eimeria maxima on maturation, differentiation, and immunogenic functions of dendritic cells derived from chicken spleen
- PMID: 33142449
- PMCID: PMC7647736
- DOI: 10.1016/j.psj.2020.07.028
In vitro effects of 5 recombinant antigens of Eimeria maxima on maturation, differentiation, and immunogenic functions of dendritic cells derived from chicken spleen
Abstract
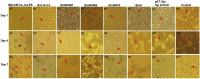
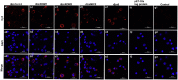
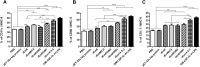
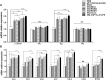
Eimeria maxima possesses integral families of immunogenic constituents that promote differentiation of immune cells during host-parasite interactions. Dendritic cells (DCs) have an irreplaceable role in the modulation of the host immunity. However, the selection of superlative antigen with immune stimulatory efficacies on host DCs is lacking. In this study, 5 recombinant proteins of E. maxima (Em), including Em14-3-3, rhomboid family domain containing proteins (ROM) EmROM1 and EmROM2, microneme protein 2 (EmMIC2), and Em8 were identified to stimulate chicken splenic derived DCs in vitro. The cultured populations were incubated with recombinant proteins, and typical morphologies of stimulated DCs were obtained. DC-associated markers major histocompatibility complex class II, CD86, CD11c, and CD1.1, showed upregulatory expressions by flow cytometry assay. Immunofluorescence assay revealed that recombinant proteins could bind with the surface of chicken splenic derived DCs. Moreover, quantitative real-time PCR results showed that distinct gene expressions of Toll-like receptors and Wnt signaling pathway were upregulated after the coincubation of recombinant proteins with DCs. The ELISA results indicated that the DCs produced a significant higher level of interleukin (IL)-12 and interferon-γ secretions after incubation with recombinant proteins. While transforming growth factor-β was significantly increased with rEmROM1, rEmROM2, and rEmMIC2 as compared to control groups, and IL-10 did not show significant alteration. Taken together, these results concluded that among 5 potential recombinant antigens, rEm14-3-3 could promote immunogenic functions of chicken splenic derived DCs more efficiently, which might represent an effective molecule for inducing the host Th1-mediated immune response against Eimeria infection.
Keywords: Eimeria maxima; chicken spleen; dendritic cell; immunogenic function; recombinant antigens.
Copyright © 2020. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Recombinant ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme of Eimeria maxima induces immunogenic maturation in chicken splenic-derived dendritic cells and drives Th1 polarization in-vitro.Microb Pathog. 2020 Jun;143:104162. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2020.104162. Epub 2020 Mar 17. Microb Pathog. 2020. PMID: 32194180
-
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase from Eimeria acervulina modulates the functions of chicken dendritic cells to boost Th1 type immune response and stimulates autologous CD4+ T cells differentiation in-vitro.Vet Res. 2020 Nov 17;51(1):138. doi: 10.1186/s13567-020-00864-z. Vet Res. 2020. PMID: 33203464 Free PMC article.
-
Rhomboid protein 2 of Eimeria maxima provided partial protection against infection by homologous species.Vet Res. 2021 Feb 18;52(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s13567-020-00886-7. Vet Res. 2021. PMID: 33602319 Free PMC article.
-
Eimeria tenella 14-kDa phosphohistidine phosphatase stimulates maturation of chicken dendritic cells and mediates DC-induced T cell priming in a Th1 cytokine interface.Res Vet Sci. 2022 Dec 20;152:61-71. doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2022.07.022. Epub 2022 Jul 27. Res Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 35932590
-
Actin-depolymerizing factor from Eimeria tenella promotes immunogenic function of chicken dendritic cells.Parasitol Res. 2021 Feb;120(2):579-592. doi: 10.1007/s00436-020-07016-4. Epub 2021 Jan 13. Parasitol Res. 2021. PMID: 33438042
Cited by
-
Expression of IL-1β in transgenic Eimeria necatrix enhances the immunogenicity of parasites and promotes mucosal immunity against coccidiosis.Front Immunol. 2024 Aug 16;15:1435702. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1435702. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39221251 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of different combination of pam2CSK4, poly (I:C) and imiquimod enhance immune responses to H9N2 avian influenza antigen in dendritic cells and duck.PLoS One. 2022 Jul 19;17(7):e0271746. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0271746. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35853030 Free PMC article.
-
Expression profile of Toll-like receptors and cytokines in the cecal tonsil of chickens challenged with Eimeria tenella.Parasitol Res. 2024 Oct 10;123(10):347. doi: 10.1007/s00436-024-08371-2. Parasitol Res. 2024. PMID: 39387973
References
-
- Ahmad T.A., El-Sayed B.A., El-Sayed L.H. Development of immunization trials against Eimeria spp. Trials Vaccinol. 2016;5:38–47.
-
- Blake D.P., Pastor-Fernández I., Nolan M.J., Tomley F.M. Recombinant anticoccidial vaccines - a cup half full? Infect. Genet. Evol. 2017;55:358–365. - PubMed
-
- Blake D.P., Tomley F.M. Securing poultry production from the ever-present Eimeria challenge. Trends Parasitol. 2014;30:12–19. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

