COVID-19 Risk Management and Screening in the Penitentiary Facilities of the Salerno Province in Southern Italy
- PMID: 33142740
- PMCID: PMC7662375
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph17218033
COVID-19 Risk Management and Screening in the Penitentiary Facilities of the Salerno Province in Southern Italy
Abstract
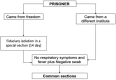
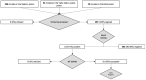
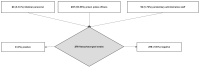
(1) Background: The emergency linked to the spread of COVID-19 in Italy has led to inevitable consequences on the penitentiary system. The risks of this emergency in prisons is mainly related to the problem of persistent overcrowding that makes social distancing difficult and the isolation of any contagion hard to arrange. The Department of Protection for Adults and Minors of the ASL Salerno Criminal Area has taken steps in order to perform screening operations and minimize the risks for prisoners and operators. (2) Methods: We conducted a two-phase observational study. In the first phase, we offered and then executed serum COVID-19 screening to all the convicted inmates. For those who had a doubtful or positive result, a swab was executed in the shortest time possible. In the second phase, a pharyngeal swab was offered and executed to all the police officers, the penitentiary administrative staff and the medical personnel working in the prison. (3) Results: In the first phase, we executed 485 COVID-19 blood tests on prisoners, 3 (0.61%) of which were positive. The three positive inmates underwent nasopharyngeal swabbing, which ultimately were negative. After that, we executed 276 nasopharyngeal swabs on the prison personnel, penitentiary administrative staff and medical personnel-all were negative. (4) Conclusion: All tests (blood tests and swabs) that were carried out on the prisoners and on the staff were negative for COVID-19. We believe that all prisons in Italy and in the world should take action to ensure preventive and control measures in order to safeguard the health of the prison population and of all the people who work there.
Keywords: COVID-19; convicted people; prevention; prison; prison workers; screening.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Mental health care in French correctional facilities during the Covid-19 pandemic].Encephale. 2020 Jun;46(3S):S60-S65. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2020.05.002. Epub 2020 May 8. Encephale. 2020. PMID: 32475693 Free PMC article. French.
-
The risk of the 'prison-emptying' effect in Italy due to the Covid-19 pandemic.Med Leg J. 2020 Jul;88(2):103-104. doi: 10.1177/0025817220923697. Epub 2020 May 15. Med Leg J. 2020. PMID: 32410516 No abstract available.
-
[Another effect of CoViD-19: turning on the lights on the Italian prison situation.].Recenti Prog Med. 2020 May;111(5):287-289. doi: 10.1701/3366.33407. Recenti Prog Med. 2020. PMID: 32448876 Italian.
-
Negative nasopharyngeal swabs in COVID-19 pneumonia: the experience of an Italian Emergengy Department (Piacenza) during the first month of the Italian epidemic.Acta Biomed. 2020 Sep 7;91(3):e2020024. doi: 10.23750/abm.v91i3.9979. Acta Biomed. 2020. PMID: 32921720 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The pandemic in prison: interventions and overisolation.Cien Saude Colet. 2020 Sep;25(9):3493-3502. doi: 10.1590/1413-81232020259.15682020. Epub 2020 Aug 28. Cien Saude Colet. 2020. PMID: 32876243 Review. English, Portuguese.
Cited by
-
Not Only COVID-19: Prevalence and Management of Latent Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Infection in Three Penitentiary Facilities in Southern Italy.Healthcare (Basel). 2022 Feb 18;10(2):386. doi: 10.3390/healthcare10020386. Healthcare (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35206999 Free PMC article.
-
Does In-Person Visiting Affect the Number of COVID-19 Cases in Prisons?Life (Basel). 2021 Nov 5;11(11):1184. doi: 10.3390/life11111184. Life (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34833060 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Evaluation of Rapid Isothermal Amplification and Antigen Assays for Screening Testing of SARS-CoV-2.Viruses. 2022 Feb 25;14(3):468. doi: 10.3390/v14030468. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35336875 Free PMC article.
-
Suicide Risk Screening and Assessment before and after the COVID-19 Pandemic in New Inmates.Healthcare (Basel). 2024 Jan 2;12(1):100. doi: 10.3390/healthcare12010100. Healthcare (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38201006 Free PMC article.
-
Malpractice Claims and Ethical Issues in Prison Health Care Related to Consent and Confidentiality.Healthcare (Basel). 2022 Jul 12;10(7):1290. doi: 10.3390/healthcare10071290. Healthcare (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35885817 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lauer S.A., Grantz K.H., Bi Q., Jones F.K., Zheng Q., Meredith H.R., Azman A.S., Reich N.G., Lessler J. The Incubation Period of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) From Publicly Reported Confirmed Cases: Estimation and Application. Ann. Intern. Med. 2020;172:577–582. doi: 10.7326/M20-0504. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources