The Novel Herbal Cocktail AGA Alleviates Oral Cancer through Inducing Apoptosis, Inhibited Migration and Promotion of Cell Cycle Arrest at SubG1 Phase
- PMID: 33142749
- PMCID: PMC7692053
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers12113214
The Novel Herbal Cocktail AGA Alleviates Oral Cancer through Inducing Apoptosis, Inhibited Migration and Promotion of Cell Cycle Arrest at SubG1 Phase
Abstract
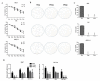
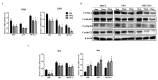
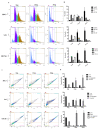
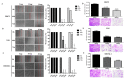
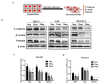
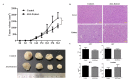
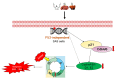
Traditional Chinese medicines Antler's extract (A) and Ganoderma lucidum (G) and Antrodia Camphorata (A) have been known to individually contain a plethora of bioactive factors including triterpenoids, polysaccharides etc., exerting various curative impacts such as anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidative, anti-atherosclerotic and anti-viral activities. However, their combinatorial therapeutic efficacy for oral cancer has not been investigated. Hence, we synthesized a robust cocktail called AGA and investigated its anti-oral cancer potential in vitro and in vivo. An MTT assay revealed the IC50 of AGA to be about 15 mg at 72 h. Therefore, 10 mg and 20 mg doses were selected to study the effect of AGA. The AGA significantly inhibited proliferation of oral cancer cells (HSC3, SAS, and OECM-1) in a dose- and time-dependent manner. AGA retarded cell cycle regulators (CDK4, CDK6, cyclin A, B1, D1 and E2) and apoptosis inhibitory protein Bcl-2, but enhanced pro-apoptotic protein Bax and a higher percentage of cells in Sub-G1 phase. Mechanistically, AGA suppressed all EMT markers; consequently, it decreased the migration ability of cancer cells. AGA significantly reduced xenograft tumor growth in nude mice with no adverse events in liver and renal toxicity. Conclusively, AGA strongly inhibited oral cancer through inducing apoptosis and inhibiting the migration and promotion of cell cycle arrest at subG1 phase, which may be mediated primarily via cocktail-contained triterpenoids and polysaccharides.
Keywords: Antler’s extract; Antrodia Camphorata; Ganoderma lucidum; anti-oxidation; cell cycle; oral cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Hung L.C., Kung P.T., Lung C.H., Tsai M.H., Liu S.A., Chiu L.T., Huang K.H., Tsai W.C. Assessment of the Risk of Oral Cancer Incidence in A High-Risk Population and Establishment of A Predictive Model for Oral Cancer Incidence Using A Population-Based Cohort in Taiwan. Int. J Environ. Res. Public Health. 2020;17:665. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17020665. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Liu H.Y., Huang C.F., Li C.H., Tsai C.Y., Chen W.H., Wei H.J., Wang M.F., Kuo Y.H., Cheong M.L., Deng W.P. Osteoporosis Recovery by Antrodia camphorata Alcohol Extracts through Bone Regeneration in SAMP8 Mice. Evid Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2016;2016:2617868. doi: 10.1155/2017/6297946. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gu L., Mo E., Yang Z., Fang Z., Sun B., Wang C., Zhu X., Bao J., Sung C. Effects of Red Deer Antlers on Cutaneous Wound Healing in Full-thickness Rat Models. Asian Australas J. Anim. Sci. 2008;21:277–290. doi: 10.5713/ajas.2008.70348. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

