In-Vitro Neutralization of the Neurotoxicity of Coastal Taipan Venom by Australian Polyvalent Antivenom: The Window of Opportunity
- PMID: 33142783
- PMCID: PMC7694127
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins12110690
In-Vitro Neutralization of the Neurotoxicity of Coastal Taipan Venom by Australian Polyvalent Antivenom: The Window of Opportunity
Abstract
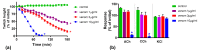
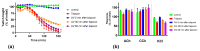
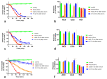
Coastal taipan (Oxyuranus scutellatus) envenoming causes life-threatening neuromuscular paralysis in humans. We studied the time period during which antivenom remains effective in preventing and arresting in vitro neuromuscular block caused by taipan venom and taipoxin. Venom showed predominant pre-synaptic neurotoxicity at 3 µg/mL and post-synaptic neurotoxicity at 10 µg/mL. Pre-synaptic neurotoxicity was prevented by addition of Australian polyvalent antivenom before the venom and taipoxin and, reversed when antivenom was added 5 min after venom and taipoxin. Antivenom only partially reversed the neurotoxicity when added 15 min after venom and had no significant effect when added 30 min after venom. In contrast, post-synaptic activity was fully reversed when antivenom was added 30 min after venom. The effect of antivenom on pre-synaptic neuromuscular block was reproduced by washing the bath at similar time intervals for 3 µg/mL, but not for 10 µg/mL. We found an approximate 10-15 min time window in which antivenom can prevent pre-synaptic neuromuscular block. This time window is likely to be longer in envenomed patients due to the delay in venom absorption. Similar effectiveness of antivenom and washing with 3 µg/mL venom suggests that antivenom most likely acts by neutralizing pre-synaptic toxins before they interfere with neurotransmission inside the motor nerve terminals.
Keywords: antivenom; paralysis; post-synaptic; pre-synaptic; taipan; venom.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The effects of antivenom on the in vitro neurotoxicity of venoms from the taipans Oxyuranus scutellatus, Oxyuranus microlepidotus and Oxyuranus scutellatus canni.Toxicon. 1999 Dec;37(12):1771-8. doi: 10.1016/s0041-0101(99)00118-x. Toxicon. 1999. PMID: 10519654
-
Neutralization of the neuromuscular inhibition of venom and taipoxin from the taipan (Oxyuranus scutellatus) by F(ab')2 and whole IgG antivenoms.Toxicol Lett. 2016 Jan 22;241:175-83. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2015.11.020. Epub 2015 Nov 24. Toxicol Lett. 2016. PMID: 26621539
-
Geographical venom variations of the Southeast Asian monocled cobra (Naja kaouthia): venom-induced neuromuscular depression and antivenom neutralization.Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2016 Jul-Aug;185-186:77-86. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpc.2016.03.005. Epub 2016 Mar 10. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26972756
-
Envenoming by a captive inland taipan, Oxyuranus microlepidotus (McCoy, 1879), Elapidae. A case report, observations on clinical efficacy of expired antivenom and review of O. microlepidotus envenoming.Toxicon. 2025 Jan;254:108210. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2024.108210. Epub 2024 Dec 16. Toxicon. 2025. PMID: 39674408 Review.
-
Antivenom for Neuromuscular Paralysis Resulting From Snake Envenoming.Toxins (Basel). 2017 Apr 19;9(4):143. doi: 10.3390/toxins9040143. Toxins (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28422078 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of Indian Polyvalent Antivenom in the Prevention and Reversal of Local Myotoxicity Induced by Common Cobra (Naja naja) Venom from Sri Lanka In Vitro.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Apr 26;13(5):308. doi: 10.3390/toxins13050308. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33926022 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Australian and Asian Commercial Antivenoms in Reversing the Post-Synaptic Neurotoxicity of O. hannah, N. naja and N. kaouthia Venoms In Vitro.Toxins (Basel). 2022 Apr 13;14(4):277. doi: 10.3390/toxins14040277. Toxins (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35448886 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro Efficacy of Antivenom and Varespladib in Neutralising Chinese Russell's Viper (Daboia siamensis) Venom Toxicity.Toxins (Basel). 2023 Jan 11;15(1):62. doi: 10.3390/toxins15010062. Toxins (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36668882 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro Neurotoxicity of Chinese Krait (Bungarus multicinctus) Venom and Neutralization by Antivenoms.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Jan 11;13(1):49. doi: 10.3390/toxins13010049. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33440641 Free PMC article.
-
A Comparison of the Efficacy of Antivenoms and Varespladib against the In Vitro Pre-Synaptic Neurotoxicity of Thai and Javanese Russell's Viper (Daboia spp.) Venoms.Toxins (Basel). 2024 Mar 1;16(3):124. doi: 10.3390/toxins16030124. Toxins (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38535790 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

