A Powerful LAMP Weapon against the Threat of the Quarantine Plant Pathogen Curtobacterium flaccumfaciens pv. flaccumfaciens
- PMID: 33142784
- PMCID: PMC7716198
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms8111705
A Powerful LAMP Weapon against the Threat of the Quarantine Plant Pathogen Curtobacterium flaccumfaciens pv. flaccumfaciens
Abstract
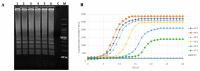
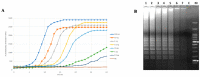
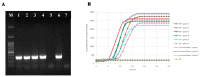
Curtobacterium flaccumfaciens pv. flaccumfaciens (Cff) is a Gram-positive phytopathogenic bacterium attacking leguminous crops and causing systemic diseases such as the bacterial wilt of beans and bacterial spot of soybeans. Since the early 20th century, Cff is reported to be present in North America, where it still causes high economic losses. Currently, Cff is an emerging plant pathogen, rapidly spreading worldwide and occurring in many bean-producing countries. Infected seeds are the main dissemination pathway for Cff, both over short and long distances. Cff remains viable in the seeds for long times, even in field conditions. According to the most recent EU legislation, Cff is included among the quarantine pests not known to occur in the Union territory, and for which the phytosanitary inspection consists mainly of the visual examination of imported bean seeds. The seedborne nature of Cff combined with the globalization of trades urgently call for the implementation of a highly specific diagnostic test for Cff, to be routinely and easily used at the official ports of entry and into the fields. This paper reports the development of a LAMP (Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification) specific for Cff, that allows the detection of Cff in infected seeds, both by fluorescence and visual monitoring, after 30 min of reaction and with a detection limit at around 4 fg/μL of pure Cff genomic DNA.
Keywords: Curtobacterium flaccumfaciens pv. flaccumfaciens; LAMP; Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification; bacterial wilt of bean; molecular diagnostics; quarantine plant pathogen; tan spot of soybean.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Bacterial wilt of dry beans caused by Curtobacterium flaccumfaciens pv. flaccumfaciens: A new threat from an old enemy.Mol Plant Pathol. 2020 May;21(5):605-621. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12926. Epub 2020 Feb 25. Mol Plant Pathol. 2020. PMID: 32097989 Free PMC article.
-
Innovative Detection of the Quarantine Plant Pathogen Curtobacterium flaccumfaciens pv. flaccumfaciens, Causal Agent of Bacterial Wilt of Leguminous Plants.Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2536:251-261. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2517-0_15. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35819609
-
PCR-based assay for the detection of Curtobacterium flaccumfaciens pv. flaccumfaciens in bean seeds.Lett Appl Microbiol. 2002;35(4):331-7. doi: 10.1046/j.1472-765x.2002.01187.x. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 12358698
-
LAMP Reaction in Plant Disease Surveillance: Applications, Challenges, and Future Perspectives.Life (Basel). 2024 Nov 26;14(12):1549. doi: 10.3390/life14121549. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39768257 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lateral flow biosensor combined with loop-mediated isothermal amplification for simple, rapid, sensitive, and reliable detection of Brucella spp.Infect Drug Resist. 2019 Jul 30;12:2343-2353. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S211644. eCollection 2019. Infect Drug Resist. 2019. PMID: 31440069 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exploiting Bacterial Pigmentation for Non-Destructive Detection of Seed-Borne Pathogens by Using Photoacoustic Techniques.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Nov 28;24(23):7616. doi: 10.3390/s24237616. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39686153 Free PMC article.
-
The Potential Use of Isothermal Amplification Assays for In-Field Diagnostics of Plant Pathogens.Plants (Basel). 2021 Nov 10;10(11):2424. doi: 10.3390/plants10112424. Plants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34834787 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current trends in management of bacterial pathogens infecting plants.Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2023 Apr;116(4):303-326. doi: 10.1007/s10482-023-01809-0. Epub 2023 Jan 23. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2023. PMID: 36683073 Review.
-
Detection and Control of Pantoea agglomerans Causing Plum Bacterial Shot-Hole Disease by Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Technique.Front Microbiol. 2022 May 25;13:896567. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.896567. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35694300 Free PMC article.
References
-
- EPPO Curtobacterium flaccumfaciens pv. flaccumfaciens. Bull. OEPP. 2011;41:320–328.
-
- EPPO Global Database Curtobacterium flaccumfaciens pv. flaccumfaciens (CORBFL) [(accessed on 28 October 2020)];2020 Categorization. Available online: https://gd.eppo.int/taxon/CORBFL/categorization.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

