BRCA1-A and BRISC: Multifunctional Molecular Machines for Ubiquitin Signaling
- PMID: 33142801
- PMCID: PMC7692841
- DOI: 10.3390/biom10111503
BRCA1-A and BRISC: Multifunctional Molecular Machines for Ubiquitin Signaling
Abstract
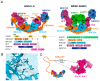
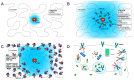
The K63-linkage specific deubiquitinase BRCC36 forms the core of two multi-subunit deubiquitination complexes: BRCA1-A and BRISC. BRCA1-A is recruited to DNA repair foci, edits ubiquitin signals on chromatin, and sequesters BRCA1 away from the site of damage, suppressing homologous recombination by limiting resection. BRISC forms a complex with metabolic enzyme SHMT2 and regulates the immune response, mitosis, and hematopoiesis. Almost two decades of research have revealed how BRCA1-A and BRISC use the same core of subunits to perform very distinct biological tasks.
Keywords: BRCA1; BRCC36; DNA repair; RAP80; SHMT2; SUMO; deubiquitination; immune regulation; ubiquitin.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Polge C., Uttenweiler-Joseph S., Leulmi R., Heng A.E., Burlet-Schiltz O., Attaix D., Taillandier D. Deciphering the ubiquitin proteome: Limits and advantages of high throughput global affinity purification-mass spectrometry approaches. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2013;45:2136–2146. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2013.05.031. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

