Masked Phenolic-Selenium Conjugates: Potent and Selective Antiproliferative Agents Overcoming P-gp Resistance
- PMID: 33142908
- PMCID: PMC7692337
- DOI: 10.3390/ph13110358
Masked Phenolic-Selenium Conjugates: Potent and Selective Antiproliferative Agents Overcoming P-gp Resistance
Abstract
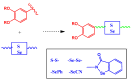
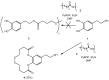
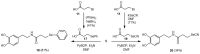
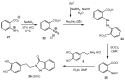
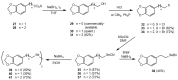
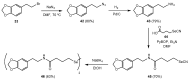
Cancer accounts for one of the most complex diseases nowadays due to its multifactorial nature. Despite the vast number of cytotoxic agents developed so far, good therapeutic approaches are not always reached. In recent years, multitarget drugs are gaining great attention against multifactorial diseases in contraposition to polypharmacy. Herein we have accomplished the conjugation of phenolic derivatives with an ample number of organochalcogen motifs with the aim of developing novel antiproliferative agents. Their antioxidant, and antiproliferative properties (against six tumour and one non-tumour cell lines) were analysed. Moreover, in order to predict P-gp-mediated chemoresistance, the P-glycoprotein assay was also conducted in order to determine whether compounds prepared herein could behave as substrates of that glycoprotein. Selenium derivatives were found to be significantly stronger antiproliferative agents than their sulfur isosters. Moreover, the length and the nature of the tether, together with the nature of the organoselenium scaffold were also found to be crucial features in the observed bioactivities. The lead compound, bearing a methylenedioxyphenyl moiety, and a diselenide functionality, showed a good activity (GI50 = 0.88‒2.0 µM) and selectivity towards tumour cell lines (selectivity index: 14‒32); moreover, compounds considered herein were not substrates for the P-gp efflux pump, thus avoiding the development of chemoresistance coming from such mechanism, commonly found for widely-used chemotherapeutic agents.
Keywords: P-gp; antioxidant; antiproliferative; organoselenium; phenolics.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
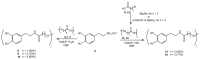

Similar articles
-
Biotinylated selenocyanates: Potent and selective cytostatic agents.Bioorg Chem. 2023 Apr;133:106410. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2023.106410. Epub 2023 Feb 8. Bioorg Chem. 2023. PMID: 36822000
-
Selenocoumarins as new multitarget antiproliferative agents: Synthesis, biological evaluation and in silico calculations.Eur J Med Chem. 2019 Oct 1;179:493-501. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.06.073. Epub 2019 Jun 27. Eur J Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 31271961
-
Chalcogen-containing phenolics as antiproliferative agents.Future Med Chem. 2018 Feb 1;10(3):319-334. doi: 10.4155/fmc-2017-0053. Epub 2018 Feb 5. Future Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 29400087
-
Cancer cell permeability-glycoprotein as a target of MDR reverters: possible role of novel dihydropyridine derivatives.Curr Drug Targets. 2006 Aug;7(8):949-59. doi: 10.2174/138945006778019336. Curr Drug Targets. 2006. PMID: 16918323 Review.
-
Overcoming tumor multidrug resistance using drugs able to evade P-glycoprotein or to exploit its expression.Med Res Rev. 2012 Nov;32(6):1220-62. doi: 10.1002/med.20239. Epub 2011 Mar 3. Med Res Rev. 2012. PMID: 21374643 Review.
Cited by
-
Chemoselective Preparation of New Families of Phenolic-Organoselenium Hybrids-A Biological Assessment.Molecules. 2022 Feb 15;27(4):1315. doi: 10.3390/molecules27041315. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35209105 Free PMC article.
-
Selenonium Salt as a Catalyst for Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions in Water: Synthesis of Thiocyanites and Selenocyanates.Molecules. 2023 Mar 29;28(7):3056. doi: 10.3390/molecules28073056. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37049818 Free PMC article.
-
Role of natural P-gp inhibitor in the effective delivery for chemotherapeutic agents.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023 Jan;149(1):367-391. doi: 10.1007/s00432-022-04387-2. Epub 2022 Oct 21. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36269390 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thio- and selenosemicarbazones as antiprotozoal agents against Trypanosoma cruzi and Trichomonas vaginalis.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2022 Dec;37(1):781-791. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2022.2041629. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 35193444 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Chemistry and Applications of Thio-, Seleno-, and Tellurosugars.Molecules. 2025 May 5;30(9):2053. doi: 10.3390/molecules30092053. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40363858 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- López Ó., Merino-Montiel P., Fernández-Bolaños J.G. Synthesis of organoselenium derivatives of biological relevance. In: Preedy V.R., editor. Selenium: Chemistry, Analysis, Function and Effect. RSC; Cambridge, UK: 2015. pp. 40–64.
-
- Kumar S., Sharma N., Maurya I.K., Bhasin A.K.K., Wangoo N., Brandão P., Felix V., Bhasin K.K., Sharma R.K. Facile synthesis, structural evaluation, antimicrobial activity and synergistic effects of novel imidazo[1, 2- a] pyridine based organoselenium compounds. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016;123:916–924. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2016.07.076. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Birmann P.T., Sousa F.S.S., de Oliveira D.H., Domingues M., Vieira B.M., Lenardão E.J., Savegnago L. 3-(4-Chlorophenylselanyl)-1-methyl-1H-indole, a new selenium compound elicits an antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory effect in mice. Eur. J. Pharm. 2018;827:71–79. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2018.03.005. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

