Liquid Crystalline Nanoparticles for Nasal Delivery of Rosuvastatin: Implications on Therapeutic Efficacy in Management of Epilepsy
- PMID: 33143084
- PMCID: PMC7693896
- DOI: 10.3390/ph13110356
Liquid Crystalline Nanoparticles for Nasal Delivery of Rosuvastatin: Implications on Therapeutic Efficacy in Management of Epilepsy
Abstract
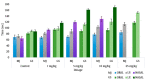
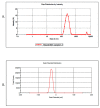
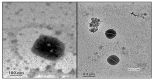
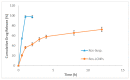
In the present study we investigated the protective role of intranasal rosuvastatin liquid crystalline nanoparticles (Ros-LCNPs) against pentylenetetrazole (PTZ) induced seizures, increasing current electroshock (ICES) induced seizures, and PTZ-induced status epilepticus. From the dose titration study, it was evident that intranasal rosuvastatin (ROS), at lower dose, was more effective than oral and intraperitoneal ROS. The Ros-LCNPs equivalent to 5 mg/kg ROS were developed by hydrotrope method using glyceryl monooleate (GMO) as lipid phase. The high resolution TEM revealed that the formed Ros-LCNPs were cubic shaped and multivesicular with mean size of 219.15 ± 8.14 nm. The Ros-LCNPs showed entrapment efficiency of 70.30 ± 1.84% and release was found to be biphasic following Korsmeyer-Peppas kinetics. Intranasal Ros-LCNPs (5 mg/kg) showed significant increase in latency to PTZ-induced seizures and ICES seizure threshold compared to control and intranasal ROS solution. Additionally, intranasal Ros-LCNPs provided effective protection against PTZ-induced status epilepticus. No impairment in cognitive functions was observed following intranasal Ros-LCNPs. The results suggested that Ros-LCNPs could be an effective and promising therapeutics for the epilepsy management.
Keywords: epilepsy; intranasal delivery; liquid crystalline nanoparticles; rosuvastatin; seizures; status epilepticus.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Citraro R., Chimirri S., Aiello R., Gallelli L., Trimboli F., Britti D., De Sarro G., Russo E. Protective effects of some statins on epileptogenesis and depressive-like behavior in WAG/Rij rats, a genetic animal model of absence epilepsy. Epilepsia. 2014;55:1284–1291. doi: 10.1111/epi.12686. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Moezi L., Shafaroodi H., Hassanipour M., Fakhrzad A., Hassanpour S., Dehpour A.R. Chronic administration of atorvastatin induced anti-convulsant effects in mice: The role of nitric oxide. Epilepsy Behav. E&B. 2012;23:399–404. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

