Hypoxia Regulates DPP4 Expression, Proteolytic Inactivation, and Shedding from Ovarian Cancer Cells
- PMID: 33143089
- PMCID: PMC7672561
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21218110
Hypoxia Regulates DPP4 Expression, Proteolytic Inactivation, and Shedding from Ovarian Cancer Cells
Abstract
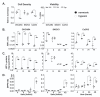
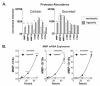
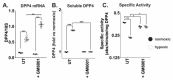
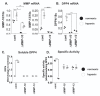
The treatment of ovarian cancer has not significantly changed in decades and it remains one of the most lethal malignancies in women. The serine protease dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP4) plays key roles in metabolism and immunity, and its expression has been associated with either pro- or anti-tumour effects in multiple tumour types. In this study, we provide the first evidence that DPP4 expression and enzyme activity are uncoupled under hypoxic conditions in ovarian cancer cells. Whilst we identified strong up-regulation of DPP4 mRNA expression under hypoxic growth, the specific activity of secreted DPP4 was paradoxically decreased. Further investigation revealed matrix metalloproteinases (MMP)-dependent inactivation and proteolytic shedding of DPP4 from the cell surface, mediated by at least MMP10 and MMP13. This is the first report of uncoupled DPP4 expression and activity in ovarian cancer cells, and suggests a previously unrecognized, cell- and tissue-type-dependent mechanism for the regulation of DPP4 in solid tumours. Further studies are necessary to identify the functional consequences of DPP4 processing and its potential prognostic or therapeutic value.
Keywords: DPP4; MMP; hypoxia; ovarian cancer; tumour microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Zhang H., Maqsudi S., Rainczuk A., Duffield N., Lawrence J., Keane F.M., Justa-Schuch D., Geiss-Friedlander R., Gorrell M.D., Stephens A.N. Identification of novel dipeptidyl peptidase 9 substrates by two-dimensional differential in-gel electrophoresis. FEBS J. 2015;282:3737–3757. doi: 10.1111/febs.13371. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

