Blood Vessel Imaging at Pre-Larval Stages of Zebrafish Embryonic Development
- PMID: 33143148
- PMCID: PMC7692510
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics10110886
Blood Vessel Imaging at Pre-Larval Stages of Zebrafish Embryonic Development
Abstract
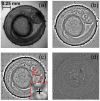
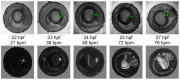
The zebrafish (Danio rerio) is an increasingly popular animal model biological system. In cardiovascular research, it has been used to model specific cardiac phenomena as well as to identify novel therapies for human cardiovascular disease. While the zebrafish cardiovascular system functioning is well examined at larval stages, the mechanisms by which vessel activity is initiated remain a subject of intense investigation. In this research, we report on an in vivo stain-free blood vessel imaging technique at pre-larval stages of zebrafish embryonic development. We have developed the algorithm for the enhancement, alignment and spatiotemporal analysis of bright-field microscopy images of zebrafish embryos. It enables the detection, mapping and quantitative characterization of cardiac activity across the whole specimen. To validate the proposed approach, we have analyzed multiple data cubes, calculated vessel images and evaluated blood flow velocity and heart rate dynamics in the absence of any anesthesia. This non-invasive technique may shed light on the mechanism of vessel activity initiation and stabilization as well as the cardiovascular system's susceptibility to environmental stressors at early developmental stages.
Keywords: cardiovascular system; embryonic development; in vivo imaging; non-invasive measurements; optical mapping; zebrafish.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A multi-endpoint in vivo larval zebrafish (Danio rerio) model for the assessment of integrated cardiovascular function.J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 2014 Jan-Feb;69(1):30-8. doi: 10.1016/j.vascn.2013.10.002. Epub 2013 Oct 16. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 2014. PMID: 24140389
-
Open access tool and microfluidic devices for phenotypic quantification of heart function of intact fruit fly and zebrafish larvae.Comput Biol Med. 2021 May;132:104314. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.104314. Epub 2021 Mar 7. Comput Biol Med. 2021. PMID: 33774273
-
Light Sheet Microscopy of Fast Cardiac Dynamics in Zebrafish Embryos.J Vis Exp. 2021 Aug 13;(174). doi: 10.3791/62741. J Vis Exp. 2021. PMID: 34459808
-
Cardio-respiratory control during early development in the model animal zebrafish.Acta Histochem. 2009;111(3):230-43. doi: 10.1016/j.acthis.2008.11.005. Epub 2009 Jan 3. Acta Histochem. 2009. PMID: 19121852 Review.
-
Developmental plasticity in the cardiovascular system of fish, with special reference to the zebrafish.Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol. 2002 Nov;133(3):547-53. doi: 10.1016/s1095-6433(02)00194-0. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol. 2002. PMID: 12443913 Review.
Cited by
-
Optical Diagnostics in Human Diseases.Diagnostics (Basel). 2021 May 12;11(5):873. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11050873. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34066215 Free PMC article.
-
Convergence of coronary artery disease genes onto endothelial cell programs.Nature. 2024 Feb;626(8000):799-807. doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-07022-x. Epub 2024 Feb 7. Nature. 2024. PMID: 38326615 Free PMC article.
-
Coagulation Factor IIIa (f3a) Knockdown in Zebrafish Leads to Defective Angiogenesis and Mild Bleeding Phenotype.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Mar 21;10:852989. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.852989. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35386206 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

