Transcriptional Analysis of Carotenoids Accumulation and Metabolism in a Pink-Fleshed Lemon Mutant
- PMID: 33143225
- PMCID: PMC7692314
- DOI: 10.3390/genes11111294
Transcriptional Analysis of Carotenoids Accumulation and Metabolism in a Pink-Fleshed Lemon Mutant
Abstract
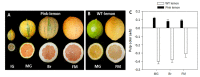
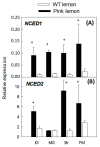
Pink lemon is a spontaneous bud mutation of lemon (Citrus limon, L. Burm. f) characterized by the production of pink-fleshed fruits due to an unusual accumulation of lycopene. To elucidate the genetic determinism of the altered pigmentation, comparative carotenoid profiling and transcriptional analysis of both the genes involved in carotenoid precursors and metabolism, and the proteins related to carotenoid-sequestering structures were performed in pink-fleshed lemon and its wild-type. The carotenoid profile of pink lemon pulp is characterized by an increased accumulation of linear carotenoids, such as lycopene, phytoene and phytofluene, from the early stages of development, reaching their maximum in mature green fruits. The distinctive phenotype of pink lemon is associated with an up-regulation and down-regulation of the genes upstream and downstream the lycopene cyclase, respectively. In particular, 9-cis epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase genes were overexpressed in pink lemon compared with the wild-type, suggesting an altered regulation of abscisic acid biosynthesis. Similarly, during early development of the fruits, genes of the carotenoid-associated proteins heat shock protein 21, fibrillin 1 and 2 and orange gene were overexpressed in the pulp of the pink-fleshed lemon compared to the wild-type, indicating its increased capacity for sequestration, stabilization or accumulation of carotenes. Altogether, the results highlighted significant differences at the transcriptomic level between the pink-fleshed lemon and its wild-type, in terms of carotenoid metabolism and the capacity of stabilization in storage structures between the two accessions. Such changes may be either responsible for the altered carotenoid accumulation or in contrast, a metabolic consequence.
Keywords: Citrus limon; carotenoids; citrus; fruit quality; gene expression; lycopene; pigments.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Rodriguez-Concepcion M., Avalos J., Bonet M.L., Boronat A., Gomez-Gomez L., Hornero-Mendez D., Limon M.C., Meléndez-Martínez A.J., Olmedilla-Alonso B., Palou A., et al. A global perspective on carotenoids: Metabolism, biotechnology, and benefits for nutrition and health. Prog. Lipid Res. 2018;70:62–93. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2018.04.004. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rodrigo M.J., Alquézar B., Alós E., Lado J., Zacarías L. Biochemical bases and molecular regulation of pigmentation in the peel of Citrus fruit. Sci. Hortic. 2013;163:46–62. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2013.08.014. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

