A Microfluidic Chip Architecture Enabling a Hypoxic Microenvironment and Nitric Oxide Delivery in Cell Culture
- PMID: 33143339
- PMCID: PMC7692389
- DOI: 10.3390/mi11110979
A Microfluidic Chip Architecture Enabling a Hypoxic Microenvironment and Nitric Oxide Delivery in Cell Culture
Abstract
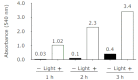
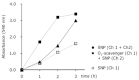
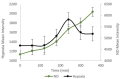
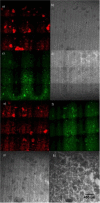
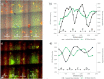
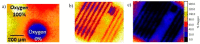
A hypoxic (low oxygen level) microenvironment and nitric oxide paracrine signaling play important roles in the control of both biological and pathological cell responses. In this study, we present a microfluidic chip architecture for nitric oxide delivery under a hypoxic microenvironment in human embryonic kidney cells (HEK-293). The chip utilizes two separate, but interdigitated microfluidic channels. The hypoxic microenvironment was created by sodium sulfite as the oxygen scavenger in one of the channels. The nitric oxide microenvironment was created by sodium nitroprusside as the light-activated nitric oxide donor in the other channel. The solutions are separated from the cell culture by a 30 µm thick gas-permeable, but liquid-impermeable polydimethylsiloxane membrane. We show that the architecture is preliminarily feasible to define the gaseous microenvironment of a cell culture in the 100 µm and 1 mm length scales.
Keywords: cell culture; gasotransmitter; hypoxia; microenvironment; microfluidic chip; nitric oxide; oxygen depletion; sodium nitroprusside.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A microfluidic oxygen sink to create a targeted cellular hypoxic microenvironment under ambient atmospheric conditions.Acta Biomater. 2018 Jun;73:167-179. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2018.04.007. Epub 2018 Apr 9. Acta Biomater. 2018. PMID: 29649636
-
Compartmentalized organ-on-a-chip structure for spatiotemporal control of oxygen microenvironments.Biomed Microdevices. 2022 Oct 21;24(4):34. doi: 10.1007/s10544-022-00634-y. Biomed Microdevices. 2022. PMID: 36269438 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced release of nitric oxide causes increased cytotoxicity of S-nitroso-N-acetyl-DL-penicillamine and sodium nitroprusside under hypoxic conditions.Biochem J. 1996 Sep 15;318 ( Pt 3)(Pt 3):789-95. doi: 10.1042/bj3180789. Biochem J. 1996. PMID: 8836121 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of Bone Hypoxic Microenvironment Based on Bone-on-a-Chip Platforms.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 10;24(8):6999. doi: 10.3390/ijms24086999. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37108162 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxygen control with microfluidics.Lab Chip. 2014 Nov 21;14(22):4305-18. doi: 10.1039/c4lc00853g. Lab Chip. 2014. PMID: 25251498 Review.
Cited by
-
Discrepancies on the Role of Oxygen Gradient and Culture Condition on Mesenchymal Stem Cell Fate.Adv Healthc Mater. 2021 Mar;10(6):e2002058. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202002058. Epub 2021 Feb 2. Adv Healthc Mater. 2021. PMID: 33533187 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Micro-engineering and nano-engineering approaches to investigate tumour ecosystems.Nat Rev Cancer. 2023 Sep;23(9):581-599. doi: 10.1038/s41568-023-00593-3. Epub 2023 Jun 23. Nat Rev Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37353679 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of microfluidic chips in anticancer drug screening.Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2022 Jun 1;22(3):302-314. doi: 10.17305/bjbms.2021.6484. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 34627135 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insight into Hypoxia Stemness Control.Cells. 2021 Aug 22;10(8):2161. doi: 10.3390/cells10082161. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34440930 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vitro models as tools for screening treatment options of head and neck cancer.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Sep 7;9:971726. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.971726. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36160162 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wang R. Overview of Gasotransmitters and the Related Signaling Network. Gasotransmitters. 2018:1–28. doi: 10.1039/9781788013000-00001. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

