Bovine Leukemia Virus Infection Affects Host Gene Expression Associated with DNA Mismatch Repair
- PMID: 33143351
- PMCID: PMC7694100
- DOI: 10.3390/pathogens9110909
Bovine Leukemia Virus Infection Affects Host Gene Expression Associated with DNA Mismatch Repair
Abstract
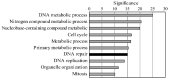
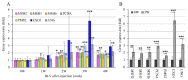
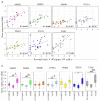
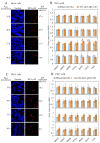
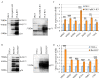
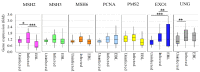
Bovine leukemia virus (BLV) causes enzootic bovine leukosis, a malignant form of B-cell lymphoma, and is closely related to human T-cell leukemia viruses. We investigated whether BLV infection affects host genes associated with DNA mismatch repair (MMR). Next-generation sequencing of blood samples from five calves experimentally infected with BLV revealed the highest expression levels of seven MMR genes (EXO1, UNG, PCNA, MSH2, MSH3, MSH6, and PMS2) at the point of peak proviral loads (PVLs). Furthermore, MMR gene expression was only upregulated in cattle with higher PVLs. In particular, the expression levels of MSH2, MSH3, and UNG positively correlated with PVL in vivo. The expression levels of all seven MMR genes in pig kidney-15 cells and the levels of PMS2 and EXO1 in HeLa cells also increased tendencies after transient transfection with a BLV infectious clone. Moreover, MMR gene expression levels were significantly higher in BLV-expressing cell lines compared with those in the respective parental cell lines. Expression levels of MSH2 and EXO1 in BLV-infected cattle with lymphoma were significantly lower and higher, respectively, compared with those in infected cattle in vivo. These results reveal that BLV infection affects MMR gene expression, offering new candidate markers for lymphoma diagnosis.
Keywords: DNA mismatch repair; bovine leukemia virus; gene expression; lymphoma stage; proviral load; viral protein expression.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Risk factors associated with increased bovine leukemia virus proviral load in infected cattle in Japan from 2012 to 2014.Virus Res. 2015 Dec 2;210:283-90. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2015.08.020. Epub 2015 Aug 29. Virus Res. 2015. PMID: 26321160
-
Relationship between Allelic Heterozygosity in BoLA-DRB3 and Proviral Loads in Bovine Leukemia Virus-Infected Cattle.Animals (Basel). 2021 Mar 1;11(3):647. doi: 10.3390/ani11030647. Animals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33804456 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping of CD4+ T-cell epitopes in bovine leukemia virus from five cattle with differential susceptibilities to bovine leukemia virus disease progression.Virol J. 2019 Dec 16;16(1):157. doi: 10.1186/s12985-019-1259-9. Virol J. 2019. PMID: 31842930 Free PMC article.
-
Detrimental effect of bovine leukemia virus (BLV) on the immunological state of cattle.Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1996 Nov;54(1-4):293-302. doi: 10.1016/s0165-2427(96)05706-6. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1996. PMID: 8988875 Review.
-
Bovine Leukemia Virus Infection in Neonatal Calves. Risk Factors and Control Measures.Front Vet Sci. 2018 Oct 25;5:267. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2018.00267. eCollection 2018. Front Vet Sci. 2018. PMID: 30410920 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Kinetic Study of BLV Infectivity in BLV Susceptible and Resistant Cattle in Japan from 2017 to 2019.Pathogens. 2021 Oct 5;10(10):1281. doi: 10.3390/pathogens10101281. Pathogens. 2021. PMID: 34684230 Free PMC article.
-
Interrelated Oncogenic Viruses and Breast Cancer.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Mar 28;9:781111. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.781111. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35419411 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of Bovine Leukemia Virus-Induced Lymphoma with BoLA-DRB3 Polymorphisms at DNA, Amino Acid, and Binding Pocket Property Levels.Pathogens. 2021 Apr 6;10(4):437. doi: 10.3390/pathogens10040437. Pathogens. 2021. PMID: 33917549 Free PMC article.
-
The bioinformatics analysis and experimental validation of the carcinogenic role of EXO1 in lung adenocarcinoma.Front Oncol. 2024 Dec 24;14:1492725. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1492725. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39777332 Free PMC article.
-
Bovine Leukaemia Virus: Current Epidemiological Circumstance and Future Prospective.Viruses. 2021 Oct 27;13(11):2167. doi: 10.3390/v13112167. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34834973 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
- A (16H02590)/Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (A) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS)
- 16930548/Grant from the Project of the NARO Bio-oriented Technology Research Advancement Institution
- 9151615/Grant from the program for the promotion of Basic and Applied Research for Innovations in the Biooriented Industry
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

