Recipient vessel selection for head and neck reconstruction: A 30-year experience in a single institution
- PMID: 33143393
- PMCID: PMC7644354
- DOI: 10.7181/acfs.2020.00339
Recipient vessel selection for head and neck reconstruction: A 30-year experience in a single institution
Abstract
Background: The advance in microsurgical technique has facilitated a proper approach for reconstruction of extensive head and neck defects. For the success of free tissue reconstruction, selection of the recipient vessel is one of the most important factors. However, the vascular anatomy of this region is very complex, and a clear guideline about this subject is still lacking. In this study, we present our 30 years of experiences of free tissue reconstruction for head and neck defects.
Methods: In this retrospective study, we analyzed a total of 138 flaps in 127 patients who underwent head and neck reconstruction using free tissue transfer following tumor resection between October 1986 to August 2019. Patients who underwent facial palsy reconstruction were excluded. Medical records including patient's demographics, detailed operation notes, follow-up records, and photographs were collected and analyzed.
Results: Among a total of 127 patients, 10 patients underwent a secondary operation due to cancer recurrence. The most commonly used type of flap was radial forearm flap (n= 107), followed by the anterolateral thigh flap (n= 18) and fibula flap (n= 10). With regard to recipient vessels, superior thyroid artery was most commonly used in arterial anastomosis (58.7%), and internal jugular vein (51.3%) was the first choice for venous anastomosis. The flap survival rate was 100%. Four cases of venous thrombosis were resolved with thrombectomy and re-anastomosis.
Conclusion: Superior thyroid artery and internal jugular vein were reliable choices as recipient vessels. Proper recipient vessel selection could improve the result of head and neck reconstruction.
Keywords: Free tissue flap; Head and neck cancer; Microsurgery; Neck dissection.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
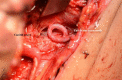
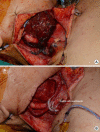
References
-
- Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin DM. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 2010;127:2893–917. - PubMed
-
- Serletti JM, Higgins JP, Moran S, Orlando GS. Factors affecting outcome in free-tissue transfer in the elderly. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2000;106:66–70. - PubMed
-
- Colen LB, Stevenson A, Sidorov V, Potparic Z, Pacelli E, Searles J, et al. Microvascular anastomotic thrombosis in experimental diabetes mellitus. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1997;99:156–62. - PubMed
-
- Bengtson BP, Schusterman MA, Baldwin BJ, Miller MJ, Reece GP, Kroll SS, et al. Influence of prior radiotherapy on the development of postoperative complications and success of free tissue transfers in head and neck cancer reconstruction. Am J Surg. 1993;166:326–30. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

