Sonographic appearance of syphilitic induration mimicking squamous cell carcinoma in the lower lip: a case report
- PMID: 33143735
- PMCID: PMC7641852
- DOI: 10.1186/s13256-020-02547-x
Sonographic appearance of syphilitic induration mimicking squamous cell carcinoma in the lower lip: a case report
Abstract
Background: Syphilis is a sexually transmitted disease caused by the spirochete Treponema pallidum. Recently, its incidence has been increasing worldwide. We encountered a young woman who presented with induration mimicking squamous cell carcinoma in the lower lip, without major medical conditions.
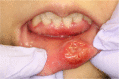
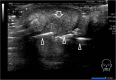
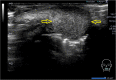
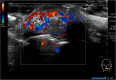
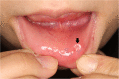
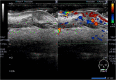
Case presentation: A 25-year-old Japanese woman presented with a 1-month history of a painless induration in her lower lip. Because squamous cell carcinoma was suspected, a preoperation work up was performed, including laboratory tests, an ultrasonographic examination, and a biopsy. The ultrasonography findings showed an oval-shaped 17 × 11 × 12 mm tumor-like lesion with heterogeneous internal echo and an indistinct border. A pressure test and color Doppler sonography revealed that the lesion was soft with a very abundant blood flow. These findings suggested the possibility of underlying inflammatory causes rather than a neoplastic tumor. Serology tests for syphilis, including the anti-Treponema pallidum antibody and reactive rapid plasma reagin tests, were positive. The biopsy revealed no malignancy. Finally, she was diagnosed as having primary syphilis and treated with amoxicillin for 28 days. The rapid plasma reagin value gradually decreased and the initial induration in her lower lip disappeared.
Conclusion: This case highlights the need for prompt examinations for possible underlying infective causes, such as syphilis, when seeing a painless induration with ulcer in the lip. Ultrasonography was helpful in the differential diagnosis of a tumor-like lesion and should be included in addition to syphilis serology tests, such as anti-Treponema pallidum antibody and rapid plasma reagin tests.
Keywords: Case report; Color Doppler ultrasonography; Dental clinic; Lower lip; Pressure test; Syphilis; Ultrasonography.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Multiple primary syphilis on the lip, nipple-areola and penis: An immunohistochemical examination of Treponema pallidum localization using an anti-T. pallidum antibody.J Dermatol. 2015 May;42(5):515-7. doi: 10.1111/1346-8138.12818. Epub 2015 Feb 24. J Dermatol. 2015. PMID: 25708895
-
Primary Syphilis Presenting As a Chronic Lip Ulcer.Cureus. 2020 Feb 24;12(2):e7086. doi: 10.7759/cureus.7086. Cureus. 2020. PMID: 32226687 Free PMC article.
-
[Nodular granuloma of the lip. An unusual manifestation of secondary syphilis].Hautarzt. 2013 Oct;64(10):722-4. doi: 10.1007/s00105-013-2641-y. Hautarzt. 2013. PMID: 23979072 German.
-
Syphilitic hepatitis: a case report and review of the literature.BMC Gastroenterol. 2019 Nov 19;19(1):191. doi: 10.1186/s12876-019-1112-z. BMC Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 31744461 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Primary syphilis with initial lower-lip sclerosis--a case report].Nihon Jibiinkoka Gakkai Kaiho. 2010 Sep;113(9):758-61. doi: 10.3950/jibiinkoka.113.758. Nihon Jibiinkoka Gakkai Kaiho. 2010. PMID: 20954363 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Ultrasonographic Characteristics in the Fingers and Other Superficial Glomus Tumours.Dermatol Res Pract. 2023 Jul 26;2023:7126799. doi: 10.1155/2023/7126799. eCollection 2023. Dermatol Res Pract. 2023. PMID: 37546347 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Notification Trends Among Syphilis Cases in Japan. National Institute of Infectious Diseases (NIID). https://www.niid.go.jp/niid/ja/syphilism/syphilis-trend.html. Accessed 16 July 2020.
-
- Regezi JA, Sciubba JJ, Jordan RCK. Oral pathology: clinical pathologic correlations. 7. St. Louis: Elsevier; 2016. Ulcerative conditions: syphilis; p. 28.
-
- Scott CM, Flint SR. Oral syphilis--re-emergence of an old disease with oral manifestations. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2005;34:58–63. - PubMed
-
- Asai S, Sato S, Okami K, Takanashi N, Umezawa K, Dadinsuren A, et al. Sonographic evaluation of the treatment response of the submandibular glands in patients with immunoglobulin G4-related disease. J Ultrasound Med. 2015;34:783–788. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

