Thyroid Dysfunction and Atherosclerosis: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 33144416
- PMCID: PMC7811672
- DOI: 10.21873/invivo.12147
Thyroid Dysfunction and Atherosclerosis: A Systematic Review
Abstract
Background/aim: Thyroid dysfunction, both hypo- and hyperthyroidism, has been associated with cardiovascular disease. The aim of this study was to evaluate the association between thyroid dysfunction and atherosclerosis measured mostly by carotid intima-media thickness, as well as discuss whether L-T4 replacement is able to reverse or slow down the progression of atherosclerosis.
Materials and methods: The review was conducted according the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis (PRISMA) guidelines. We performed on PubMed a literature search from May 2004 to January 2020, using the search terms 'subclinical hypothyroidism' or 'thyroid disorders' and 'carotid artery', 'carotid intima-media thickness (IMT)', 'levothyroxine', and 'atherosclerosis'.
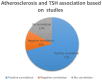
Results: Twenty-six studies were eligible and included in the analysis. Overall, the studies encompassed a total of 36.434 patients included in this review. Most studies indicated a proportional correlation between IMT and thyroid dysfunction. Levothyroxine (L-T4) replacement led to significant decrease of IMT after 1 year in most studies.
Conclusion: Most studies have concluded that thyroid dysfunction is associated with arterial wall remodeling and, thus, with increased cardiovascular risk. However, the exact mechanistic background of pathological structural changes in the arterial wall is still unsettled. Large randomized controlled studies are required to definitively address the extent to which T4 replacement therapy might benefit patients with subclinical thyroid disorders.
Keywords: Subclinical hypothyroidism; atherosclerosis; carotid artery; carotid intima-media thickness; levothyroxine; review; thyroid disorders.
Copyright© 2020, International Institute of Anticancer Research (Dr. George J. Delinasios), All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The Authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of levothyroxine on the progression of carotid intima-media thickness in subclinical hypothyroidism patients: a meta-analysis.BMJ Open. 2017 Oct 22;7(10):e016053. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-016053. BMJ Open. 2017. PMID: 29061604 Free PMC article. Review.
-
No evidence of association between subclinical thyroid disorders and common carotid intima medial thickness or atherosclerotic plaque.Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2015 Dec;25(12):1104-10. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2015.09.001. Epub 2015 Oct 21. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2015. PMID: 26615224 Free PMC article.
-
Subclinical hypothyroidism is associated with higher carotid intima-media thickness in cross-sectional analysis of the Brazilian Longitudinal Study of Adult Health (ELSA-Brasil).Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2016 Oct;26(10):915-21. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2016.06.005. Epub 2016 Jun 20. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2016. PMID: 27389191
-
Regression of the increased common carotid artery-intima media thickness in subclinical hypothyroidism after thyroid hormone replacement.Endocr J. 2009;56(6):753-8. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.k09e-049. Epub 2009 Jun 9. Endocr J. 2009. PMID: 19506325
-
[Cardiovascular remodelling in patients with sub-clinical hypothyroidism].Minerva Cardioangiol. 2006 Dec;54(6):807-10. Minerva Cardioangiol. 2006. PMID: 17396336 Review. Italian.
Cited by
-
Lipoprotein Ratios: Correlation With Glycated Hemoglobin (HbA1c) Among Thyroid Disorders' Patients.Cureus. 2024 Feb 14;16(2):e54191. doi: 10.7759/cureus.54191. eCollection 2024 Feb. Cureus. 2024. Retraction in: Cureus. 2025 Jan 10;17(1):r158. doi: 10.7759/cureus.r158. PMID: 38496179 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Mechanisms and Management of Thyroid Disease and Atrial Fibrillation: Impact of Atrial Electrical Remodeling and Cardiac Fibrosis.Cells. 2022 Dec 14;11(24):4047. doi: 10.3390/cells11244047. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36552815 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The relationship between atherosclerotic disease and relapse during ATD treatment.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Oct 28;9:1039829. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.1039829. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 36386359 Free PMC article.
-
Association Between Thyroid Parameters and Subclinical Atherosclerosis in Hospitalised Euthyroid Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2023 Oct 12;16:3163-3171. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S429941. eCollection 2023. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2023. PMID: 37849978 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac manifestations in hyperthyroidism.Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Apr 11;23(4):136. doi: 10.31083/j.rcm2304136. eCollection 2022 Apr. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 39076244 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cabral MD, Teixeira P, Soares D, Leite S, Salles E, Waisman M. Effects of thyroxine replacement on endothelial function and carotid artery intima-media thickness in female patients with mild subclinical hypothyroidism. Clinics (Sao Paulo) 2011;66(8):1321–1328. doi: 10.1590/s1807-59322011000800003. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Delitala AP, Filigheddu F, Orrù M, AlGhatrif M, Steri M, Pilia MG, Scuteri A, Lobina M, Piras MG, Delitala G, Lakatta EG, Schlessinger D, Cucca F. No evidence of association between subclinical thyroid disorders and common carotid intima medial thickness or atherosclerotic plaque. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2015;25(12):1104–1110. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2015.09.001. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical