Cryopreservation of Biologically Functional Submandibular Gland Rudiments from Fetal Mice
- PMID: 33144433
- PMCID: PMC7811606
- DOI: 10.21873/invivo.12164
Cryopreservation of Biologically Functional Submandibular Gland Rudiments from Fetal Mice
Abstract
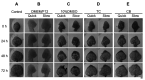
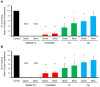
Background/aim: Cryopreservation of cell lines has been widely used in the laboratory; however, cryopreservation of organs is still considered to be difficult. The submandibular gland (SMG) of fetal mice is one of the best-characterized organs. We investigated the conditions for cryopreserving SMG rudiments.
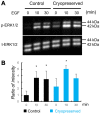
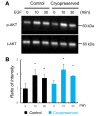
Materials and methods: Embryonic day 13 SMG rudiments were cryopreserved with or without a cryoprotectant. They were thawed and incubated in DMEM/F12 medium. Moreover, the influence of EGF stimulation on the signaling cascade after frozen-thawing the rudiments was analyzed by Western blotting.
Results: When SMG rudiments were cryopreserved without a cryoprotectant, all cells in the rudiments died. However, the SMG rudiments that had been preserved in a cryoprotectant showed branching morphogenesis. Additionally, the responsiveness of signaling cascades to EGF did not differ between frozen with a cryoprotectant and non-frozen rudiments.
Conclusion: Cryopreservation might be a useful technology for preserving tissues from small organs, such as fetal SMG rudiments.
Keywords: AKT; Cryopreservation; EGF; ERK1/2; branching morphogenesis; submandibular gland.
Copyright© 2020, International Institute of Anticancer Research (Dr. George J. Delinasios), All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The Authors have no conflicts of interest to declare regarding this study.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The ERK-1/2 signaling pathway is involved in the stimulation of branching morphogenesis of fetal mouse submandibular glands by EGF.Dev Biol. 2000 Apr 15;220(2):183-96. doi: 10.1006/dbio.2000.9639. Dev Biol. 2000. PMID: 10753509
-
Extracellular regulated kinase5 is expressed in fetal mouse submandibular glands and is phosphorylated in response to epidermal growth factor and other ligands of the ErbB family of receptors.Dev Growth Differ. 2012 Dec;54(9):801-8. doi: 10.1111/dgd.12008. Epub 2012 Oct 19. Dev Growth Differ. 2012. PMID: 23078124
-
Shh/Ptch and EGF/ErbB cooperatively regulate branching morphogenesis of fetal mouse submandibular glands.Dev Biol. 2016 Apr 15;412(2):278-87. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2016.02.018. Epub 2016 Mar 2. Dev Biol. 2016. PMID: 26930157
-
Regulatory mechanisms of branching morphogenesis in mouse submandibular gland rudiments.Jpn Dent Sci Rev. 2018 Feb;54(1):2-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jdsr.2017.06.002. Epub 2018 Mar 17. Jpn Dent Sci Rev. 2018. PMID: 29628996 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Branching morphogenesis in the fetal mouse submandibular gland is codependent on growth factors and extracellular matrix.J Med Invest. 2009;56 Suppl:228-33. doi: 10.2152/jmi.56.228. J Med Invest. 2009. PMID: 20224186 Review.
References
-
- Rapats G, Luyet B. Patterns of ice formation in aqueous solutions of glycerol. Biodynamica. 1966;10(198):1–68. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
