The NF-κB/leukemia inhibitory factor/STAT3 signaling pathway in antibody-mediated suppression of Sindbis virus replication in neurons
- PMID: 33144502
- PMCID: PMC7682347
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2016691117
The NF-κB/leukemia inhibitory factor/STAT3 signaling pathway in antibody-mediated suppression of Sindbis virus replication in neurons
Abstract
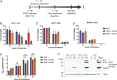
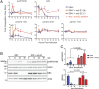
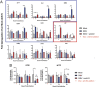
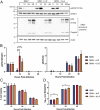
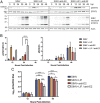
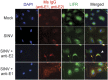
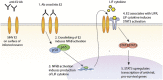
Alphaviruses are positive-sense, enveloped RNA viruses that are important causes of viral encephalomyelitis. Sindbis virus (SINV) is the prototype alphavirus and preferentially infects neurons in rodents to induce an encephalomyelitis similar to the human disease. Using a mouse model of SINV infection of the nervous system, many of the immune processes involved in recovery from viral encephalomyelitis have been identified. Antibody specific to the SINV E2 glycoprotein plays an important role in recovery and is sufficient for noncytolytic suppression of virus replication in vivo and in vitro. To investigate the mechanism of anti-E2 antibody-mediated viral suppression, a reverse-phase protein array was used to broadly survey cellular signaling pathway activation following antibody treatment of SINV-infected differentiated AP-7 neuronal cells. Anti-E2 antibody induced rapid transient NF-κB and later sustained Y705 STAT3 phosphorylation, outlining an intracellular signaling cascade activated by antiviral antibody. Because NF-κB target genes include the STAT3-activating IL-6 family cytokines, expression of these messenger RNAS (mRNAs) was assessed. Expression of leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) cytokine mRNA, but not other IL-6 family member mRNAs, was up-regulated by anti-E2 antibody. LIF induced STAT3 Y705 phosphorylation in infected differentiated AP-7 cells but did not inhibit virus replication. However, anti-E2 antibody localized the LIF receptor to areas of E2 expression on the infected cell surface, and LIF enhanced the antiviral effects of antibody. These findings identify activation of the NF-κB/LIF/STAT3 signaling cascade as involved in inducing antibody-mediated viral suppression and highlight the importance of nonneutralizing antibody functions in viral clearance from neurons.
Keywords: alphavirus; encephalomyelitis; virus clearance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Treatment of Sindbis Virus-Infected Neurons with Antibody to E2 Alters Synthesis of Complete and nsP1-Expressing Defective Viral RNAs.mBio. 2022 Oct 26;13(5):e0222122. doi: 10.1128/mbio.02221-22. Epub 2022 Sep 7. mBio. 2022. PMID: 36069441 Free PMC article.
-
NF-κB Activation Promotes Alphavirus Replication in Mature Neurons.J Virol. 2019 Nov 26;93(24):e01071-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01071-19. Print 2019 Dec 15. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 31554691 Free PMC article.
-
Germ Line IgM Is Sufficient, but Not Required, for Antibody-Mediated Alphavirus Clearance from the Central Nervous System.J Virol. 2018 Mar 14;92(7):e02081-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02081-17. Print 2018 Apr 1. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29321331 Free PMC article.
-
The role of antibody in recovery from alphavirus encephalitis.Immunol Rev. 1997 Oct;159:155-61. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1997.tb01013.x. Immunol Rev. 1997. PMID: 9416509 Review.
-
Recovery from viral encephalomyelitis: immune-mediated noncytolytic virus clearance from neurons.Immunol Res. 2010 Jul;47(1-3):123-33. doi: 10.1007/s12026-009-8143-4. Immunol Res. 2010. PMID: 20087684 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Drosophila as a Model for Human Viral Neuroinfections.Cells. 2022 Aug 29;11(17):2685. doi: 10.3390/cells11172685. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36078091 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The use of RNA-based treatments in the field of cancer immunotherapy.Mol Cancer. 2023 Jul 7;22(1):106. doi: 10.1186/s12943-023-01807-w. Mol Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37420174 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treatment of Sindbis Virus-Infected Neurons with Antibody to E2 Alters Synthesis of Complete and nsP1-Expressing Defective Viral RNAs.mBio. 2022 Oct 26;13(5):e0222122. doi: 10.1128/mbio.02221-22. Epub 2022 Sep 7. mBio. 2022. PMID: 36069441 Free PMC article.
-
mtSTAT3 suppresses rheumatoid arthritis by regulating Th17 and synovial fibroblast inflammatory cell death with IL-17-mediated autophagy dysfunction.Exp Mol Med. 2025 Feb;57(1):221-234. doi: 10.1038/s12276-024-01376-y. Epub 2025 Jan 17. Exp Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 39825104 Free PMC article.
-
From the Friend to the Foe-Enterococcus faecalis Diverse Impact on the Human Immune System.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 19;25(4):2422. doi: 10.3390/ijms25042422. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38397099 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

