Combined treatment of mitoxantrone sensitizes breast cancer cells to rapalogs through blocking eEF-2K-mediated activation of Akt and autophagy
- PMID: 33144562
- PMCID: PMC7642277
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-020-03153-x
Combined treatment of mitoxantrone sensitizes breast cancer cells to rapalogs through blocking eEF-2K-mediated activation of Akt and autophagy
Abstract
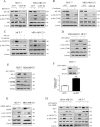
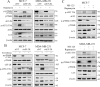
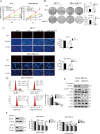
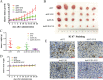
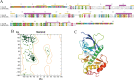
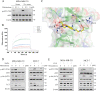
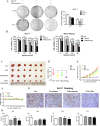
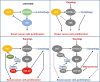
Oncogenic activation of the mTOR signaling pathway occurs frequently in tumor cells and contributes to the devastating features of cancer, including breast cancer. mTOR inhibitors rapalogs are promising anticancer agents in clinical trials; however, rapalogs resistance remains an unresolved clinical challenge. Therefore, understanding the mechanisms by which cells become resistant to rapalogs may guide the development of successful mTOR-targeted cancer therapy. In this study, we found that eEF-2K, which is overexpressed in cancer cells and is required for survival of stressed cells, was involved in the negative-feedback activation of Akt and cytoprotective autophagy induction in breast cancer cells in response to mTOR inhibitors. Therefore, disruption of eEF-2K simultaneously abrogates the two critical resistance signaling pathways, sensitizing breast cancer cells to rapalogs. Importantly, we identified mitoxantrone, an admitted anticancer drug for a wide range of tumors, as a potential inhibitor of eEF-2K via a structure-based virtual screening strategy. We further demonstrated that mitoxantrone binds to eEF-2K and inhibits its activity, and the combination treatment of mitoxantrone and mTOR inhibitor resulted in significant synergistic cytotoxicity in breast cancer. In conclusion, we report that eEF-2K contributes to the activation of resistance signaling pathways of mTOR inhibitor, suggesting a novel strategy to enhance mTOR-targeted cancer therapy through combining mitoxantrone, an eEF-2K inhibitor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeted silencing of elongation factor 2 kinase suppresses growth and sensitizes tumors to doxorubicin in an orthotopic model of breast cancer.PLoS One. 2012;7(7):e41171. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0041171. Epub 2012 Jul 20. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22911754 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of eEF-2K-mediated autophagy enhances the cytotoxicity of raddeanin A against human breast cancer cells in vitro.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2018 Apr;39(4):642-648. doi: 10.1038/aps.2017.139. Epub 2017 Dec 14. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2018. PMID: 29239350 Free PMC article.
-
Thymoquinone inhibits cell proliferation, migration, and invasion by regulating the elongation factor 2 kinase (eEF-2K) signaling axis in triple-negative breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2018 Oct;171(3):593-605. doi: 10.1007/s10549-018-4847-2. Epub 2018 Jul 3. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2018. PMID: 29971628
-
What is the impact of eukaryotic elongation factor 2 kinase on cancer: A systematic review.Eur J Pharmacol. 2019 Aug 15;857:172470. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.172470. Epub 2019 Jun 18. Eur J Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31226250
-
Novel approaches for molecular targeted therapy of breast cancer: interfering with PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2013 Feb;13(2):188-204. doi: 10.2174/1568009611313020008. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2013. PMID: 23215720 Review.
Cited by
-
Design and Characterization of a Novel eEF2K Degrader with Potent Therapeutic Efficacy Against Triple-Negative Breast Cancer.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Feb;11(5):e2305035. doi: 10.1002/advs.202305035. Epub 2023 Dec 12. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 38084501 Free PMC article.
-
Signaling pathways in cancer metabolism: mechanisms and therapeutic targets.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023 May 10;8(1):196. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01442-3. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023. PMID: 37164974 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sodium tanshinone IIA sulphate inhibits angiogenesis in lung adenocarcinoma via mediation of miR-874/eEF-2K/TG2 axis.Pharm Biol. 2023 Dec;61(1):868-877. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2023.2204879. Pharm Biol. 2023. PMID: 37300283 Free PMC article.
-
Harnessing artificial intelligence to identify Bufalin as a molecular glue degrader of estrogen receptor alpha.Nat Commun. 2025 Aug 22;16(1):7854. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-62288-7. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40846852
-
Insights into the computer-aided drug design and discovery based on anthraquinone scaffold for cancer treatment: A systematic review.PLoS One. 2024 May 22;19(5):e0301396. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0301396. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38776291 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

