Differences in serum protein electrophoretic pattern in dogs naturally infected with Babesia gibsoni and Babesia canis
- PMID: 33144631
- PMCID: PMC7609656
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-75908-7
Differences in serum protein electrophoretic pattern in dogs naturally infected with Babesia gibsoni and Babesia canis
Abstract
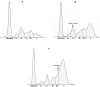
Canine babesiosis may cause several hematological and biochemical changes, but only limited studies are available regarding the possible differences of changes in animals infected by different Babesia parasites. The study focused on the evaluation of the differences in serum protein electrophoretic pattern between dogs naturally infected with B. gibsoni (17 dogs) and B. canis (40 dogs). The mean values of total proteins, β1-, β2- and γ-globulins were in dogs infected with B. gibsoni significantly higher (P < 0.05 and P < 0.001) than in dogs infected with B. canis. The relative concentrations of albumin, α1-, α2-globulins and the A/G ratios were in the B. gibsoni infected dogs significantly lower (P < 0.001), no significant differences were found in the relative concentrations of β1- and β2-globulins. Significant differences were found in most of the evaluated parameters when comparing the results in relation to the form of B. canis infection to B. gibsoni infection. Hematological indices showed significant differences between dogs infected with B. gibsoni and the complicated form of B. canis infection. In conclusion, the obtained results suggest differences in the changes of serum protein electrophoretic pattern between dogs infected with both Babesia species and thus, in the response to the infection caused by various Babesia parasites.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Adaszek L, et al. The first case of Babesia gibsoni infection in a dog in Poland. Vet. Med. (Czech) 2018;63:225–228. doi: 10.17221/155/2017-VETMED. - DOI
-
- Ishimine T, Makimura S, Kitazawa S, Tamura S, Suzuki N. Pathophysiological findings on blood of beagles experimentally infected with Babesia gibsoni. Jpn. J. Tropical Med. Hyg. 1978;6:15–26. doi: 10.2149/tmh1973.6.15. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources