A new method for accurately localizing and resecting pulmonary nodules
- PMID: 33145071
- PMCID: PMC7578447
- DOI: 10.21037/jtd-20-2089
A new method for accurately localizing and resecting pulmonary nodules
Abstract
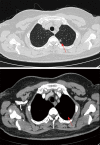
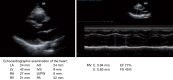
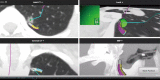
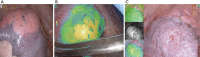
With the use of low-dose CT for early screening of lung cancer, more and more early lung cancers are found. At the same time, patients with small lung nodules have also increased, it is a great challenge for surgeons to resect pulmonary nodules with small volume, deep position and no solid components under video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery. Many studies have reported preoperative and intraoperative methods for localizing lung nodules before minimally invasive resection. Methods for preoperative localization include CT-guided hook-wire positioning, coil positioning, or dye injection and radionuclide location Methods for intraoperative localization include intraoperative ultrasound localization and tactile pressure-sensing localization. After the localization of pulmonary nodules under the guidance of CT patients need to restrict their activities; otherwise, it is easy for the nodules to move, causing the operation to fail, and may also cause complications such as pneumothorax, puncture site pain, and pulmonary parenchymal bleeding. In the past, we injected melamine dye under the guidance of electromagnetic navigation bronchoscope to locate lung nodules. The purpose of this case is introducing a new method for accurately localizing and resecting pulmonary nodules by injecting indocyanine green (ICG) under the guidance of electromagnetic navigation bronchoscope and the resection of small pulmonary nodules under the fluoroscope.
Keywords: Pulmonary nodules; electromagnetic navigation bronchoscope; fluoroscope; indocyanine green (ICG).
2020 Journal of Thoracic Disease. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/jtd-20-2089). CSN reports Consultant & Advisory Board for Siemens Healthineer; Consultant & Advisory Board for Medtronic; Consultant & Advisory Board for Johnson & Johnson; Consultant & Advisory Board for Stryker. CS Ng also serves as an unpaid editorial board member of Journal of Thoracic Disease from Feb 2019 to Jan 2021. MPK reports personal fees from Veran, personal fees from Medtronics, personal fees from Intuitive Surgical, outside the submitted work. MP Kim also serves as an unpaid editorial board member of Journal of Thoracic Disease from Sep 2018 – Aug 2020. SL reports personal fees from OLYMPUS, personal fees from FUJIFILM, personal fees from BOSTON Scientific, personal fees from Ambu, outside the submitted work. M Sato serves as an unpaid editorial board member of Journal of Thoracic Disease from Oct 2018 to Sep 2020.
Figures



Comment in
-
Treatment strategy of EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer.J Thorac Dis. 2022 Mar;14(3):602-606. doi: 10.21037/jtd-22-177. J Thorac Dis. 2022. PMID: 35399242 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Future prospects of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR-TKIs) and surgery for non-small cell lung cancer.J Thorac Dis. 2022 Apr;14(4):809-811. doi: 10.21037/jtd-22-57. J Thorac Dis. 2022. PMID: 35572861 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Recent advances in electromagnetic navigation bronchoscopy for localization of peripheral pulmonary nodules.J Thorac Dis. 2022 Apr;14(4):802-804. doi: 10.21037/jtd-22-179. J Thorac Dis. 2022. PMID: 35572872 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Intratumoral and intertumoral heterogeneity drives EGFR treatment considerations.J Thorac Dis. 2022 May;14(5):1299-1301. doi: 10.21037/jtd-22-312. J Thorac Dis. 2022. PMID: 35693600 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Diagnostic methods to localize pulmonary nodules and management of pleural infection after lobectomy.J Thorac Dis. 2022 May;14(5):1302-1305. doi: 10.21037/jtd-22-180. J Thorac Dis. 2022. PMID: 35693604 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Critical points in the management of EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer.J Thorac Dis. 2022 Jun;14(6):1748-1752. doi: 10.21037/jtd-22-269. J Thorac Dis. 2022. PMID: 35813737 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Diagnosis and treatment of non-small cell lung cancer: current advances and challenges.J Thorac Dis. 2022 Jun;14(6):1753-1757. doi: 10.21037/jtd-22-364. J Thorac Dis. 2022. PMID: 35813756 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The emerging landscape of EFGR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in lung adenocarcinoma-successes and challenges.J Thorac Dis. 2022 Jun;14(6):1766-1771. doi: 10.21037/jtd-22-432. J Thorac Dis. 2022. PMID: 35813761 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries [published correction appears in CA Cancer J Clin. 2020 Jul;70(4):313]. CA Cancer J Clin 2018;68:394-424. 10.3322/caac.21492 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
