Thoracic imaging finding of rheumatic diseases
- PMID: 33145088
- PMCID: PMC7578499
- DOI: 10.21037/jtd.2020.04.16
Thoracic imaging finding of rheumatic diseases
Abstract
In the era of Precision Medicine, diagnostic imaging plays a key role in initial diagnosis and treatment response assessment in thoracic manifestation of various rheumatic disorders; resulting in increased dependency on imaging for treatment planning. Chest radiographs serve as a good initial screening tool for assessment of emergent and urgent thoracic conditions, e.g., pneumothorax, pulmonary edema, consolidation and pleural effusions. Cross-sectional imaging techniques, e.g., computed tomography (CT) and positron emission tomography-computed tomography (PET-CT) are most commonly utilized to evaluate more detailed pulmonary and mediastinal manifestations of rheumatic conditions. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and ultrasound are most commonly used in cardiovascular, neural and musculoskeletal structures. This review article aims to highly key common thoracic imaging findings of rheumatic disorders, highlighting imaging test of choice for the particular disorder.
Keywords: Rheumatology; giant cell arteritis (GCA); granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA); microscopic polyangiitis (MPA); radiology; rheumatoid arthritis; sarcoidosis.
2020 Journal of Thoracic Disease. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The series “Role of Precision Imaging in Thoracic Disease” was commissioned by the editorial office without any funding or sponsorship. The authors have no other conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
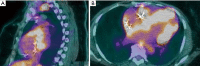

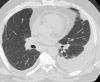
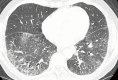

References
-
- Collins J, Stern EJ. Chest radiology, the essentials. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. (2007) ISBN:0781763142.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
