Differential expression of genes related to calcineurin and mTOR signaling and regulatory miRNAs in peripheral blood from kidney recipients under tacrolimus-based therapy
- PMID: 33145270
- PMCID: PMC7575939
- DOI: 10.21037/atm-20-1757
Differential expression of genes related to calcineurin and mTOR signaling and regulatory miRNAs in peripheral blood from kidney recipients under tacrolimus-based therapy
Abstract
Background: Genetic and epigenetics factors have been implicated in drug response, graft function and rejection in solid organ transplantation. Differential expression of genes involved in calcineurin and mTOR signaling pathway and regulatory miRNAs was analyzed in the peripheral blood of kidney recipient cohort (n=36) under tacrolimus-based therapy.
Methods: PPP3CA, PPP3CB, MTOR, FKBP1A, FKBP1B and FKBP5 mRNA expression and polymorphisms in PPP3CA and MTOR were analyzed by qPCR. Expression of miRNAs targeting PPP3CA (miR-30a, miR-145), PPP3CB (miR-10b), MTOR (miR-99a, miR-100), and FKBP1A (miR-103a) was measured by qPCR array.
Results: PPP3CA and MTOR mRNA levels were reduced in the first three months of treatment compared to pre-transplant (P<0.05). PPP3CB, FKBP1A, FKBP1B, and FKBP5 expression was not changed. In the 3rd month of treatment, the expression of miR-99a, which targets MTOR, increased compared to pre-transplant (P<0.05). PPP3CA c.249G>A (GG genotype) and MTOR c.2997C>T (TT genotype) were associated with reduced expression of PPP3CA mRNA and MTOR, respectively. FKBP1B mRNA levels were higher in patients with acute rejection (P=0.026).
Conclusions: The expression of PPP3CA, MTOR and miR-99a in the peripheral blood of renal recipients is influenced by tacrolimus-based therapy and by PPP3CA and MTOR variants. These molecules can be potential biomarkers for pharmacotherapy monitoring.
Keywords: Circulating miRNAs; gene expression; kidney transplant; pharmacogenomics.
2020 Annals of Translational Medicine. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/atm-20-1757). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures



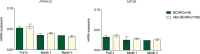
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
