Molecular Detection of Microorganisms Associated with Small Mammals and Their Ectoparasites in Mali
- PMID: 33146105
- PMCID: PMC7695096
- DOI: 10.4269/ajtmh.19-0727
Molecular Detection of Microorganisms Associated with Small Mammals and Their Ectoparasites in Mali
Abstract
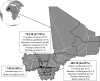
Small mammals are the natural reservoirs for many zoonotic pathogens. Using molecular tools, we assessed the prevalence of bacteria and protozoans in small mammals and their ectoparasites in Faladjè, Bougouni, and Bamoko, Mali. A total of 130 small mammals belonging to 10 different species were captured, of which 74 (56.9%) were infested by ectoparasites, including Laelaps echidnina, Xenopsylla cheopis, Amblyomma variegatum, Rhipicephalus sanguineus sensu lato, and Haemaphysalis spp. nymphs. DNA of Bartonella was found in 14/75 (18.7%), 6/48 (12.5%), and 3/7 (42.8%) small mammals from Faladjè, Bougouni, and Bamako, respectively. In Faladjè, Bartonella DNA was detected in 31/68 (45.6%) of L. echidnina and 14/22 (63.6%) of X. cheopis. In Bougouni, it was found in 2/26 (7.7%) of L. echidnina and 10/42 (23.8%) of X. cheopis. The sequences of Bartonella obtained from small mammals were close to those of Bartonella mastomydis, Bartonella elizabethae, and uncultured Bartonella spp. In Faladjè, Coxiella burnetii DNA was detected in 64.4% (29/45) of Haemaphysalis spp. ticks, 4.5% (2/44) of Mastomys erythroleucus, 12.5% (1/8) of Praomys daltoni, and 1.5% (1/68) of L. echidnina. We found DNA of Wolbachia in X. cheopis from Faladjè and DNA of Rickettsia africae and Ehrlichia ruminantium in Am. variegatum from Bougouni. The results of our study show that several small mammal species harbor and may serve as potential reservoirs of Bartonella spp., likely to play a major role in the maintenance, circulation, and potential transmission of bacteria in Mali. The pathogenicity of these bacteria for humans or animals remains to be demonstrated.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Bartonella species in small mammals and their ectoparasites in Taiwan.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2010 Oct;83(4):917-23. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.2010.10-0083. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2010. PMID: 20889892 Free PMC article.
-
The Distribution and Diversity of Bartonella Species in Rodents and Their Ectoparasites across Thailand.PLoS One. 2015 Oct 20;10(10):e0140856. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0140856. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26484537 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular evidence of vector-borne pathogens in dogs and cats and their ectoparasites in Algiers, Algeria.Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 2016 Apr;45:23-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cimid.2016.01.002. Epub 2016 Jan 23. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 2016. PMID: 27012917
-
Microorganisms associated with hedgehog arthropods.Parasit Vectors. 2023 Jun 22;16(1):211. doi: 10.1186/s13071-023-05764-7. Parasit Vectors. 2023. PMID: 37349802 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bartonella species and their ectoparasites: selective host adaptation or strain selection between the vector and the mammalian host?Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 2011 Jul;34(4):299-314. doi: 10.1016/j.cimid.2011.04.005. Epub 2011 May 25. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 2011. PMID: 21616536 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of Bed Bugs from Comoros, Using Morphological, Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionisation Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry, and Molecular Biology Tools, and the Detection of Associated Bacteria.Insects. 2025 Feb 2;16(2):148. doi: 10.3390/insects16020148. Insects. 2025. PMID: 40003778 Free PMC article.
-
Tick-Borne Diseases of Humans and Animals in West Africa.Pathogens. 2023 Oct 24;12(11):1276. doi: 10.3390/pathogens12111276. Pathogens. 2023. PMID: 38003741 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathogen Detection in Ornithodoros sonrai Ticks and Invasive House Mice Mus musculus domesticus in Senegal.Microorganisms. 2022 Nov 30;10(12):2367. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10122367. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 36557620 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Vietnamese Flea Species and Their Associated Microorganisms Using Morphological, Molecular, and Protein Profiling.Microorganisms. 2023 Mar 9;11(3):716. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11030716. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 36985289 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Survey of Rodent-Borne Infectious Agents in the Ferlo Region, Senegal.Genes (Basel). 2023 May 18;14(5):1107. doi: 10.3390/genes14051107. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37239466 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bengis RG, Leighton FA, Fischer JR, Artois M, Mörner T, Tate CM, 2004. The role of wildlife in emerging and re-emerging zoonoses. Rev Sci Tech 23: 497–511. - PubMed
-
- Heglasova I, Víchová B, Kraljik J, Mošanský L, Miklisová D, Stanko M, 2018. Molecular evidence and diversity of the spotted-fever group Rickettsia spp. in small mammals from natural, suburban and urban areas of eastern Slovakia. Ticks Tick Borne Dis 9: 1400–1406. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

