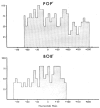
Sequences determined in the phage, prophage, and bacterial
att site region. The sequences are numbered with zero as the central base of the common region. Sequences extending rightward from zero into the P’ and B’ arms is assigned postive numbers, and leftward from 0 into the P and B arms negative numbers (———) Phage DNA: (

) and bacterial DNA; (◆ ◆) the common core region. The top section of the figure includes the central 111 bases of each of the four
att sites, 55 bases of each side of zero. The lower section includes the distal portions of the four arms, P and B from −50 toward the left, and P’ and B’ from +50 towards right. (There is 5-base overlap of each arm with the top section.) In the lower section, the central 101 bases are represented by the appropriate symbols. Three types of structural features are identified in the sequences. Molecular palindromes are indicated by (

) above the corresponding sequences in both the top and lower sections. There are no palindromes meeting the set criteria (see below) which are unique to the prophage
att sites. Direct repeats are only marked in the top section and are indicated below the corresponding sequences by (

). Dashed lines connect the pairs of repeats. In the prophage sequences only those direct repeats (see below for criteria) which are unique to these sequences, that is, those with elements in P and B’ or B and P’, are shown. Inverted repeats are only marked in the top section and are indicated by (

) above the corresponding sequences. The two elements of each inverted repeats are connected by dashed lines. The only inverted repeats included in the lower section are the three that occur in the proposed
int gene termination region (see text). The criteria used in marking each of the above sequences features were a minimum of six base pairs with no mismatches, a single central mismatch with at least three base pairs to each side. Three sequences, of special interest because of their location, have been marked as inverted repeats even though they do not meet the stated criteria. Two of these occur from −46 to −33 and from −40 to −30 in the P and b arms, respectively. The third sequences involves the core-arm junctures in the phage
att site (see text). Direct and inverted repeats, with elements often separated by considerable distance, also occur in the distal portions of the arms (lower section) but have not been included. In the central 111 base pairs, similar sequences (“identities”) occurring in approximately the same position in the P and B arms, and in the P’ and B’ arms, are marked between the two prophage sequences by (

). A sequence of ten bases (+5 to +14) in the phage
l strand (marked+++) is identical to part of an inverted repeat structure in one arm of IS
l (47). A similar but less perfect homology exists between the
r strand (+3 to −11) and the other elements of the same inverted repeat structure that occurs in the other IS
l arm (+, exact match; ⊥, purines or pyrimidine match; and ×, A-T base pair). Homology between the core-arm junctures and the 3′ end of 16
S ribosomal RNA are indicated by (●) under the matching bases (see 69).
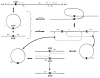



 ) bacterial DNA; (*) the relative order of these two sites is not certain; ( + ) three additional Hha I sites occur to the right of the one mapped in B’, but their locations have not been determined.
) bacterial DNA; (*) the relative order of these two sites is not certain; ( + ) three additional Hha I sites occur to the right of the one mapped in B’, but their locations have not been determined.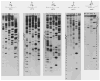

 ) bacterial DNA; (◆ ◆) common core region.
) bacterial DNA; (◆ ◆) common core region.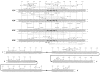
 ) and bacterial DNA; (◆ ◆) the common core region. The top section of the figure includes the central 111 bases of each of the four att sites, 55 bases of each side of zero. The lower section includes the distal portions of the four arms, P and B from −50 toward the left, and P’ and B’ from +50 towards right. (There is 5-base overlap of each arm with the top section.) In the lower section, the central 101 bases are represented by the appropriate symbols. Three types of structural features are identified in the sequences. Molecular palindromes are indicated by (
) and bacterial DNA; (◆ ◆) the common core region. The top section of the figure includes the central 111 bases of each of the four att sites, 55 bases of each side of zero. The lower section includes the distal portions of the four arms, P and B from −50 toward the left, and P’ and B’ from +50 towards right. (There is 5-base overlap of each arm with the top section.) In the lower section, the central 101 bases are represented by the appropriate symbols. Three types of structural features are identified in the sequences. Molecular palindromes are indicated by (
 ) above the corresponding sequences in both the top and lower sections. There are no palindromes meeting the set criteria (see below) which are unique to the prophage att sites. Direct repeats are only marked in the top section and are indicated below the corresponding sequences by (
) above the corresponding sequences in both the top and lower sections. There are no palindromes meeting the set criteria (see below) which are unique to the prophage att sites. Direct repeats are only marked in the top section and are indicated below the corresponding sequences by (
 ). Dashed lines connect the pairs of repeats. In the prophage sequences only those direct repeats (see below for criteria) which are unique to these sequences, that is, those with elements in P and B’ or B and P’, are shown. Inverted repeats are only marked in the top section and are indicated by (
). Dashed lines connect the pairs of repeats. In the prophage sequences only those direct repeats (see below for criteria) which are unique to these sequences, that is, those with elements in P and B’ or B and P’, are shown. Inverted repeats are only marked in the top section and are indicated by (
 ) above the corresponding sequences. The two elements of each inverted repeats are connected by dashed lines. The only inverted repeats included in the lower section are the three that occur in the proposed int gene termination region (see text). The criteria used in marking each of the above sequences features were a minimum of six base pairs with no mismatches, a single central mismatch with at least three base pairs to each side. Three sequences, of special interest because of their location, have been marked as inverted repeats even though they do not meet the stated criteria. Two of these occur from −46 to −33 and from −40 to −30 in the P and b arms, respectively. The third sequences involves the core-arm junctures in the phage att site (see text). Direct and inverted repeats, with elements often separated by considerable distance, also occur in the distal portions of the arms (lower section) but have not been included. In the central 111 base pairs, similar sequences (“identities”) occurring in approximately the same position in the P and B arms, and in the P’ and B’ arms, are marked between the two prophage sequences by (
) above the corresponding sequences. The two elements of each inverted repeats are connected by dashed lines. The only inverted repeats included in the lower section are the three that occur in the proposed int gene termination region (see text). The criteria used in marking each of the above sequences features were a minimum of six base pairs with no mismatches, a single central mismatch with at least three base pairs to each side. Three sequences, of special interest because of their location, have been marked as inverted repeats even though they do not meet the stated criteria. Two of these occur from −46 to −33 and from −40 to −30 in the P and b arms, respectively. The third sequences involves the core-arm junctures in the phage att site (see text). Direct and inverted repeats, with elements often separated by considerable distance, also occur in the distal portions of the arms (lower section) but have not been included. In the central 111 base pairs, similar sequences (“identities”) occurring in approximately the same position in the P and B arms, and in the P’ and B’ arms, are marked between the two prophage sequences by (
 ). A sequence of ten bases (+5 to +14) in the phage l strand (marked+++) is identical to part of an inverted repeat structure in one arm of ISl (47). A similar but less perfect homology exists between the r strand (+3 to −11) and the other elements of the same inverted repeat structure that occurs in the other ISl arm (+, exact match; ⊥, purines or pyrimidine match; and ×, A-T base pair). Homology between the core-arm junctures and the 3′ end of 16S ribosomal RNA are indicated by (●) under the matching bases (see 69).
). A sequence of ten bases (+5 to +14) in the phage l strand (marked+++) is identical to part of an inverted repeat structure in one arm of ISl (47). A similar but less perfect homology exists between the r strand (+3 to −11) and the other elements of the same inverted repeat structure that occurs in the other ISl arm (+, exact match; ⊥, purines or pyrimidine match; and ×, A-T base pair). Homology between the core-arm junctures and the 3′ end of 16S ribosomal RNA are indicated by (●) under the matching bases (see 69).