Arsenic induced redox imbalance triggers the unfolded protein response in the liver of zebrafish
- PMID: 33147493
- PMCID: PMC7725916
- DOI: 10.1016/j.taap.2020.115307
Arsenic induced redox imbalance triggers the unfolded protein response in the liver of zebrafish
Abstract
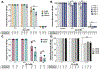
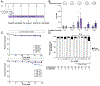
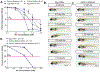
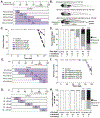
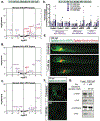
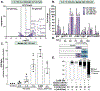
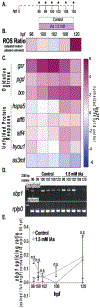
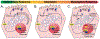
Inorganic arsenic (iAs) is one of the most endemic toxicants worldwide and oxidative stress is a key cellular pathway underlying iAs toxicity. Other cellular stress response pathways, such as the unfolded protein response (UPR), are also impacted by iAs exposure, however it is not known how these pathways intersect to cause disease. We optimized the use of zebrafish larvae to identify the relationship between these cellular stress response pathways and arsenic toxicity. We found that the window of iAs susceptibility during zebrafish development corresponds with the development of the liver, and that even a 24-h exposure can cause lethality if administered to mature larvae, but not to early embryos. Acute exposure of larvae to iAs generates reactive oxygen species (ROS), an antioxidant response, endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and UPR activation in the liver. An in vivo assay using transgenic larvae expressing a GFP-tagged secreted glycoprotein in hepatocytes (Tg(fabp10a:Gc-EGFP)) revealed acute iAs exposure selectively decreased expression of Gc-EGFP, indicating that iAs impairs secretory protein folding in the liver. The transcriptional output of UPR activation is preceded by ROS production and activation of genes involved in the oxidative stress response. These studies implicate redox imbalance as the mechanism of iAs-induced ER stress and suggest that crosstalk between these pathways underlie iAs-induced hepatic toxicity.
Keywords: Arsenic; ER stress; Liver; Oxidative stress; Unfolded protein response; Zebrafish.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Declaration of interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inorganic arsenic causes fatty liver and interacts with ethanol to cause alcoholic liver disease in zebrafish.Dis Model Mech. 2018 Feb 26;11(2):dmm031575. doi: 10.1242/dmm.031575. Dis Model Mech. 2018. PMID: 29361514 Free PMC article.
-
Ethanol metabolism and oxidative stress are required for unfolded protein response activation and steatosis in zebrafish with alcoholic liver disease.Dis Model Mech. 2013 Sep;6(5):1213-26. doi: 10.1242/dmm.012195. Epub 2013 Jun 20. Dis Model Mech. 2013. PMID: 23798569 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatic and Nephric NRF2 Pathway Up-Regulation, an Early Antioxidant Response, in Acute Arsenic-Exposed Mice.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2015 Oct 12;12(10):12628-42. doi: 10.3390/ijerph121012628. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2015. PMID: 26473898 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk between inflammatory mediators and endoplasmic reticulum stress in liver diseases.Cytokine. 2019 Dec;124:154577. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2018.10.018. Epub 2018 Nov 14. Cytokine. 2019. PMID: 30446215 Review.
-
Redox controls UPR to control redox.J Cell Sci. 2014 Sep 1;127(Pt 17):3649-58. doi: 10.1242/jcs.153643. Epub 2014 Aug 8. J Cell Sci. 2014. PMID: 25107370 Review.
Cited by
-
Exposure to Environmental Arsenic and Emerging Risk of Alzheimer's Disease: Perspective Mechanisms, Management Strategy, and Future Directions.Toxics. 2021 Aug 14;9(8):188. doi: 10.3390/toxics9080188. Toxics. 2021. PMID: 34437506 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recruitment of endoplasmic reticulum-targeted and cytosolic mRNAs into membrane-associated stress granules.RNA. 2021 Oct;27(10):1241-1256. doi: 10.1261/rna.078858.121. Epub 2021 Jul 8. RNA. 2021. PMID: 34244458 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Gentianella acuta (Michx.) Hulten against the arsenic-induced development hindrance of mouse oocytes.Biometals. 2024 Dec;37(6):1411-1430. doi: 10.1007/s10534-024-00613-1. Epub 2024 May 30. Biometals. 2024. PMID: 38814492
-
Metformin Mitigates the Impact of Arsenic Exposure on the Maternal and Offspring Reproductive System of Female Mice.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2025 Mar 22. doi: 10.1007/s12011-025-04577-2. Online ahead of print. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2025. PMID: 40119994
-
Sustained effects of developmental exposure to inorganic arsenic on hepatic gsto2 expression and mating success in zebrafish.Biol Open. 2024 Mar 1;13(3):bio060094. doi: 10.1242/bio.060094. Epub 2024 Mar 6. Biol Open. 2024. PMID: 38446164 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adeyemi JA, da Cunha Martins-Junior A, Barbosa F Jr., 2015. Teratogenicity, genotoxicity and oxidative stress in zebrafish embryos (Danio rerio) co-exposed to arsenic and atrazine. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 172-173, 7–12. - PubMed
-
- Ahamed M, Akhtar MJ, Khan MAM, Alrokayan SA, Alhadlaq HA, 2019. Oxidative stress mediated cytotoxicity and apoptosis response of bismuth oxide (Bi2O3) nanoparticles in human breast cancer (MCF-7) cells. Chemosphere 216, 823–831. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

