Inhibitor of Hyaluronic Acid Synthesis 4-Methylumbelliferone as an Anti-Inflammatory Modulator of LPS-Mediated Astrocyte Responses
- PMID: 33147798
- PMCID: PMC7662953
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21218203
Inhibitor of Hyaluronic Acid Synthesis 4-Methylumbelliferone as an Anti-Inflammatory Modulator of LPS-Mediated Astrocyte Responses
Abstract
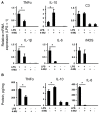
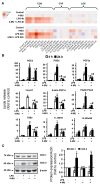
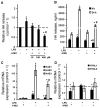
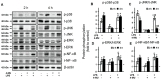
Astrocytes are glial cells that play an important role in neuroinflammation. Astrocytes respond to many pro-inflammatory stimuli, including lipopolysaccharide (LPS), an agonist of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4). Regulatory specificities of inflammatory signaling pathways are still largely unknown due to the ectodermal origin of astrocytes. Recently, we have shown that hyaluronic acid (HA) may form part of astrocyte inflammatory responses. Therefore, we tested 4-methylumbelliferone (4-MU), a specific inhibitor of HA synthesis, as a possible regulator of LPS-mediated responses. Rat primary astrocytes were treated with LPS with and without 4-MU and gene expression levels of inflammatory (interleukins 1β, (IL-1β), 6, (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor alpha TNFα,) and resolution interleukin 10 (IL-10) markers were evaluated via real-time PCR and western blot. The release of cytokines and HA was determined by ELISA. Oxylipin profiles were measured by ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS) analysis. Our data show that 4-MU (i) has anti-inflammatory effects in the course of TLR4 activation, decreasing the cytokines level TNFα, IL-6 and IL-1β and increasing IL-10, (ii) downregulates prostaglandin synthesis but not via cyclooxygenases COX-1 and COX-2 pathways, (iii) modulates HA synthesis and decreases LPS-induced HA synthase mRNA expression (HAS-1, HAS-2) but does not have an influence on HAS-3, HYAL1 and HYAL2 mRNAs; (iv) the effects of 4-MU are predominantly revealed via JNK but not p38, ERK mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) or nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-kB) pathways. For the first time, it is shown that 4-MU possesses the useful potential to regulate an inflammatory astrocyte response.
Keywords: 4-methylumbelliferone (4-MU); astrocytes; cyclooxygenase (COX); hyaluronic acid; interleukin 10 (IL-10); interleukin 6 (IL-6); neuroinflammation; oxylipins; toll-like receptors (TLRs).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of PPAR Ligands as Modulators of Resolution of Inflammation, via Their Influence on Cytokines and Oxylipins Release in Astrocytes.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 16;21(24):9577. doi: 10.3390/ijms21249577. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33339154 Free PMC article.
-
Oxylipin Profiles as Functional Characteristics of Acute Inflammatory Responses in Astrocytes Pre-Treated with IL-4, IL-10, or LPS.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Mar 5;21(5):1780. doi: 10.3390/ijms21051780. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32150861 Free PMC article.
-
High and Low Molecular Weight Hyaluronic Acid Differentially Influences Oxylipins Synthesis in Course of Neuroinflammation.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Aug 9;20(16):3894. doi: 10.3390/ijms20163894. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31405034 Free PMC article.
-
Propofol Inhibits Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Responses in Spinal Astrocytes via the Toll-Like Receptor 4/MyD88-Dependent Nuclear Factor-κB, Extracellular Signal-Regulated Protein Kinases1/2, and p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Pathways.Anesth Analg. 2015 Jun;120(6):1361-8. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000000645. Anesth Analg. 2015. PMID: 25695672
-
Tanshinone IIA suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced neuroinflammatory responses through NF-κB/MAPKs signaling pathways in human U87 astrocytoma cells.Brain Res Bull. 2020 Nov;164:136-145. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2020.08.019. Epub 2020 Aug 26. Brain Res Bull. 2020. PMID: 32860868
Cited by
-
Comparison of PPAR Ligands as Modulators of Resolution of Inflammation, via Their Influence on Cytokines and Oxylipins Release in Astrocytes.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 16;21(24):9577. doi: 10.3390/ijms21249577. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33339154 Free PMC article.
-
4-methylumbilliferon (4-MU) as a Potential Treatment Against Cerebral ischemia and Reperfusion Injury in Rats; An Experimental Study.Arch Acad Emerg Med. 2024 Sep 17;13(1):e8. doi: 10.22037/aaem.v13i1.2456. eCollection 2025. Arch Acad Emerg Med. 2024. PMID: 39465056 Free PMC article.
-
Plant-Derived Molecule 4-Methylumbelliferone Suppresses FcεRI-Mediated Mast Cell Activation and Allergic Inflammation.Molecules. 2022 Feb 27;27(5):1577. doi: 10.3390/molecules27051577. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35268679 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of the Primary Astrocyte-Enriched Cultures' Oxylipin Profiles Reduces Neurotoxicity.Metabolites. 2021 Jul 30;11(8):498. doi: 10.3390/metabo11080498. Metabolites. 2021. PMID: 34436439 Free PMC article.
-
Simple virus-free mouse models of COVID-19 pathologies and oral therapeutic intervention.iScience. 2024 Feb 13;27(3):109191. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.109191. eCollection 2024 Mar 15. iScience. 2024. PMID: 38433928 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

