Polymer Microchannel and Micromold Surface Polishing for Rapid, Low-Quantity Polydimethylsiloxane and Thermoplastic Microfluidic Device Fabrication
- PMID: 33147807
- PMCID: PMC7692984
- DOI: 10.3390/polym12112574
Polymer Microchannel and Micromold Surface Polishing for Rapid, Low-Quantity Polydimethylsiloxane and Thermoplastic Microfluidic Device Fabrication
Abstract
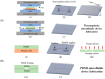
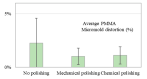
Polymer-based micromolding has been proposed as an alternative to SU-8 micromolding for microfluidic chip fabrication. However, surface defects such as milling marks may result in rough microchannels and micromolds, limiting microfluidic device performance. Therefore, we use chemical and mechanical methods for polishing polymer microchannels and micromolds. In addition, we evaluated their performance in terms of removing the machining (milling) marks on polymer microchannel and micromold surfaces. For chemical polishing, we use solvent evaporation to polish the sample surfaces. For mechanical polishing, wool felt polishing bits with an abrasive agent were employed to polish the sample surfaces. Chemical polishing reduced surface roughness from 0.38 μm (0 min, after milling) to 0.13 μm after 6 min of evaporation time. Mechanical polishing reduced surface roughness from 0.38 to 0.165 μm (optimal pressing length: 0.3 mm). As polishing causes abrasion, we evaluated sample geometry loss after polishing. Mechanically and chemically polished micromolds had optimal micromold distortion percentages of 1.01% ± 0.76% and 1.10% ± 0.80%, respectively. Compared to chemical polishing, mechanical polishing could better maintain the geometric integrity since it is locally polished by computer numerical control (CNC) miller. Using these surface polishing methods with optimized parameters, polymer micromolds and microchannels can be rapidly produced for polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) casting and thermoplastic hot embossing. In addition, low-quantity (15 times) polymer microchannel replication is demonstrated in this paper.
Keywords: PDMS casting; microchannel; micromilling; micromold; polymer microfabrication; polymer microfluidics; polymer polishing; thermoplastic hot embossing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures










References
-
- Convery N., Gadegaard N. 30 years of microfluidics. Micro Nano Eng. 2019;2:76–91. doi: 10.1016/j.mne.2019.01.003. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

