A Comprehensive Review on Source, Types, Effects, Nanotechnology, Detection, and Therapeutic Management of Reactive Carbonyl Species Associated with Various Chronic Diseases
- PMID: 33147856
- PMCID: PMC7692604
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox9111075
A Comprehensive Review on Source, Types, Effects, Nanotechnology, Detection, and Therapeutic Management of Reactive Carbonyl Species Associated with Various Chronic Diseases
Abstract
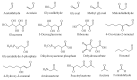
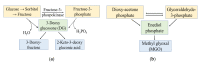
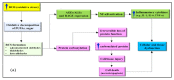
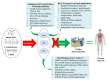
Continuous oxidation of carbohydrates, lipids, and amino acids generate extremely reactive carbonyl species (RCS). Human body comprises some important RCS namely hexanal, acrolein, 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal, methylglyoxal, malondialdehyde, isolevuglandins, and 4-oxo-2- nonenal etc. These RCS damage important cellular components including proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids, which manifests cytotoxicity, mutagenicity, multitude of adducts and crosslinks that are connected to ageing and various chronic diseases like inflammatory disease, atherosclerosis, cerebral ischemia, diabetes, cancer, neurodegenerative diseases and cardiovascular disease. The constant prevalence of RCS in living cells suggests their importance in signal transduction and gene expression. Extensive knowledge of RCS properties, metabolism and relation with metabolic diseases would assist in development of effective approach to prevent numerous chronic diseases. Treatment approaches for RCS associated diseases involve endogenous RCS metabolizers, carbonyl metabolizing enzyme inducers, and RCS scavengers. Limited bioavailability and bio efficacy of RCS sequesters suggest importance of nanoparticles and nanocarriers. Identification of RCS and screening of compounds ability to sequester RCS employ several bioassays and analytical techniques. Present review describes in-depth study of RCS sources, types, properties, identification techniques, therapeutic approaches, nanocarriers, and their role in various diseases. This study will give an idea for therapeutic development to combat the RCS associated chronic diseases.
Keywords: chronic diseases; identification; reactive carbonyl species; scavengers; treatment approach; validation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mass spectrometric approaches for the identification and quantification of reactive carbonyl species protein adducts.J Proteomics. 2013 Oct 30;92:28-50. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2013.03.030. Epub 2013 Apr 15. J Proteomics. 2013. PMID: 23597925 Review.
-
Reactive carbonyl species in vivo: generation and dual biological effects.ScientificWorldJournal. 2014 Jan 21;2014:417842. doi: 10.1155/2014/417842. eCollection 2014. ScientificWorldJournal. 2014. PMID: 24634611 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxidative and reductive metabolism of lipid-peroxidation derived carbonyls.Chem Biol Interact. 2015 Jun 5;234:261-73. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2014.12.028. Epub 2015 Jan 2. Chem Biol Interact. 2015. PMID: 25559856 Free PMC article.
-
Microbiota facilitates the formation of the aminated metabolite of green tea polyphenol (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate which trap deleterious reactive endogenous metabolites.Free Radic Biol Med. 2019 Feb 1;131:332-344. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.12.023. Epub 2018 Dec 19. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019. PMID: 30578921 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneous Determination of Multiple Reactive Carbonyl Species in High Fat Diet-Induced Metabolic Disordered Mice and the Inhibitory Effects of Rosemary on Carbonyl Stress.J Agric Food Chem. 2021 Jan 27;69(3):1123-1131. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.0c07748. Epub 2021 Jan 19. J Agric Food Chem. 2021. PMID: 33464893
Cited by
-
A mechanistic overview on green assisted formulation of nanocomposites and their multifunctional role in biomedical applications.Heliyon. 2025 Jan 8;11(3):e41654. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2025.e41654. eCollection 2025 Feb 15. Heliyon. 2025. PMID: 39916856 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reactive Carbonyl Species and Protein Adducts: Identification Strategies, Biological Mechanisms and Molecular Approaches for Their Detoxification.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Apr 28;10(5):690. doi: 10.3390/antiox10050690. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33924749 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic Effect of L-Carnosine and Hyaluronic Acid in Their Covalent Conjugates on the Antioxidant Abilities and the Mutual Defense against Enzymatic Degradation.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Mar 30;11(4):664. doi: 10.3390/antiox11040664. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35453350 Free PMC article.
-
Reactive Carbonyl Species Scavenger: Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate.Foods. 2024 Mar 25;13(7):992. doi: 10.3390/foods13070992. Foods. 2024. PMID: 38611299 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive Review of Methodology to Detect Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) in Mammalian Species and Establish Its Relationship with Antioxidants and Cancer.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Jan 18;10(1):128. doi: 10.3390/antiox10010128. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33477494 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

