SEIPIN: A Key Factor for Nuclear Lipid Droplet Generation and Lipid Homeostasis
- PMID: 33147895
- PMCID: PMC7663086
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21218208
SEIPIN: A Key Factor for Nuclear Lipid Droplet Generation and Lipid Homeostasis
Abstract
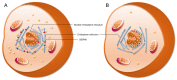
Lipid homeostasis is essential for normal cell physiology. Generally, lipids are stored in a lipid droplet (LD), a ubiquitous organelle consisting of a neutral lipid core and a single layer of phospholipid membrane. It is thought that LDs are generated from the endoplasmic reticulum and then released into the cytosol. Recent studies indicate that LDs can exist in the nucleus, where they play an important role in the maintenance of cell phospholipid homeostasis. However, the details of nuclear lipid droplet (nLD) generation have not yet been clearly characterized. SEIPIN is a nonenzymatic protein encoded by the Berardinelli-Seip congenital lipodystrophy type 2 (BSCL2) gene. It is associated with lipodystrophy diseases. Many recent studies have indicated that SEIPIN is essential for LDs generation. Here, we review much of this research in an attempt to explain the role of SEIPIN in nLD generation. From an integrative perspective, we conclude by proposing a theoretical model to explain how SEIPIN might participate in maintaining homeostasis of lipid metabolism.
Keywords: SEIPIN; lipid droplet; lipid homeostasis; nuclear.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Seipin regulates ER-lipid droplet contacts and cargo delivery.EMBO J. 2016 Dec 15;35(24):2699-2716. doi: 10.15252/embj.201695170. Epub 2016 Nov 22. EMBO J. 2016. PMID: 27879284 Free PMC article.
-
A unifying mechanism for seipin-mediated lipid droplet formation.FEBS Lett. 2024 May;598(10):1116-1126. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.14825. Epub 2024 Feb 13. FEBS Lett. 2024. PMID: 38785192 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The lipodystrophy protein seipin is found at endoplasmic reticulum lipid droplet junctions and is important for droplet morphology.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Dec 26;104(52):20890-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0704154104. Epub 2007 Dec 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 18093937 Free PMC article.
-
LDAF1 and Seipin Form a Lipid Droplet Assembly Complex.Dev Cell. 2019 Dec 2;51(5):551-563.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2019.10.006. Epub 2019 Nov 7. Dev Cell. 2019. PMID: 31708432 Free PMC article.
-
Seipin, adipogenesis and lipid droplets.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2011 Jun;22(6):204-10. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2011.02.004. Epub 2011 Apr 15. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2011. PMID: 21497513 Review.
Cited by
-
Hepatocytes Deficient in Nuclear Envelope Protein Lamina-associated Polypeptide 1 are an Ideal Mammalian System to Study Intranuclear Lipid Droplets.J Lipid Res. 2022 Oct;63(10):100277. doi: 10.1016/j.jlr.2022.100277. Epub 2022 Sep 10. J Lipid Res. 2022. PMID: 36100089 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Seipin in Human Diseases and Experimental Animal Models.Biomolecules. 2022 Jun 17;12(6):840. doi: 10.3390/biom12060840. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35740965 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of Caenorhabditis elegans in Lipid Metabolism Research.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 7;24(2):1173. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021173. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36674689 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Novel Photosensitizer for Lipid Droplet-Location Photodynamic Therapy.Front Chem. 2021 Jun 14;9:701771. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2021.701771. eCollection 2021. Front Chem. 2021. PMID: 34195177 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear Envelope Integrity in Health and Disease: Consequences on Genome Instability and Inflammation.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 6;22(14):7281. doi: 10.3390/ijms22147281. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34298904 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

