Phase I study of selinexor in combination with dexamethasone, ifosfamide, carboplatin, etoposide chemotherapy in patients with relapsed or refractory peripheral T-cell or natural-killer/T-cell lymphoma
- PMID: 33147935
- PMCID: PMC8634181
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2020.251454
Phase I study of selinexor in combination with dexamethasone, ifosfamide, carboplatin, etoposide chemotherapy in patients with relapsed or refractory peripheral T-cell or natural-killer/T-cell lymphoma
Abstract
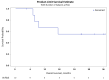
Selinexor is a selective inhibitor of nuclear export with anti-cancer properties. We performed a phase I study to determine the safety and maximum tolerated dose (MTD) of selinexor when combined with high-dose dexamethasone, ifosfamide, carboplatin and etoposide (DICE) in relapsed/refractory (R/R) T-cell lymphoma (TCL) and natural-killer/T-cell lymphoma (NKTL). Patients with R/R TCL and NKTL were treated with standard dose ICE, dexamethasone 20mg on days 3 to 7, and escalating doses of oral selinexor on days 3, 5 and 7 in a 3+3 design. Dose level (DL) 1, 2 and 3 were 40, 60 and 80mg respectively. Eleven patients with a median age of 60 were enrolled; 6 at DL1 and 5 at DL2. Patients had received a median of 2 (range 1-4) prior lines of treatment and 7 had primary refractory disease at study entry. Patients received a median of 3 cycles (range 1-6) of selinexor-DICE. The most common grade (G) 1/2 toxicities included nausea (64%), fatigue (55%), and anorexia (45%) and the most common G 3/4 toxicities included thrombocytopenia (82%), anemia (82%), neutropenia (73%), and hyponatremia (73%). Two patients developed doselimiting toxicities at DL2 and one at DL1. Five patients discontinued treatment for reasons other than disease progression or lack of response. Of the 10 evaluable patients, the overall and complete response rates were 91% and 82% respectively. The MTD of selinexor was 40mg when combined with DICE. The combination showed promising CR rates in patients with R/R TCL and NKTL but was poorly tolerated.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of ICE (ifosfamide-carboplatin-etoposide) versus DHAP (cytosine arabinoside-cisplatin-dexamethasone) as salvage chemotherapy in patients with relapsed or refractory lymphoma.Cancer Invest. 2008 May;26(4):401-6. doi: 10.1080/07357900701788098. Cancer Invest. 2008. PMID: 18443961
-
Treatment outcomes of T and natural-killer/T-cell lymphoma with ifosfamide, carboplatin and etoposide chemotherapy.Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2022 Sep;5(9):e1552. doi: 10.1002/cnr2.1552. Epub 2022 Apr 28. Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2022. PMID: 35481622 Free PMC article.
-
Ifosfamide, carboplatin, and etoposide plus granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor: a phase I study with apparent activity in non-small-cell lung cancer.J Clin Oncol. 1994 Jun;12(6):1251-8. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1994.12.6.1251. J Clin Oncol. 1994. PMID: 8201386 Clinical Trial.
-
Treatment of relapsed aggressive lymphomas: regimens with and without high-dose therapy and stem cell rescue.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2002 May;49 Suppl 1:S13-20. doi: 10.1007/s00280-002-0447-1. Epub 2002 Apr 12. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 12042984 Review.
-
Ifosfamide, carboplatin, and etoposide for neuroblastoma: a high-dose salvage regimen and review of the literature.Cancer. 2013 Feb 1;119(3):665-71. doi: 10.1002/cncr.27783. Epub 2012 Sep 5. Cancer. 2013. PMID: 22951749 Review.
Cited by
-
Novel target and treatment agents for natural killer/T-cell lymphoma.J Hematol Oncol. 2023 Jul 22;16(1):78. doi: 10.1186/s13045-023-01483-9. J Hematol Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37480137 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosome mimetics derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells deliver doxorubicin to osteosarcoma in vitro and in vivo.Drug Deliv. 2022 Dec;29(1):3291-3303. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2022.2141921. Drug Deliv. 2022. PMID: 36352741 Free PMC article.
-
Selinexor With Anti-PD-1 Antibody as a Potentially Effective Regimen for Patients With Natural Killer/T-Cell Lymphoma Failing Prior L-Asparaginase and PD-1 Blockade.Oncologist. 2024 Jan 5;29(1):e90-e96. doi: 10.1093/oncolo/oyad241. Oncologist. 2024. PMID: 37616529 Free PMC article.
-
Viral Subversion of the Chromosome Region Maintenance 1 Export Pathway and Its Consequences for the Cell Host.Viruses. 2023 Nov 6;15(11):2218. doi: 10.3390/v15112218. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 38005895 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nuclear Export in Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma and Implications for Targeted XPO1 Inhibitors.Biomolecules. 2023 Jan 5;13(1):111. doi: 10.3390/biom13010111. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 36671496 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anderson JR, Armitage JO, Weisenburger DD. Epidemiology of the non-Hodgkin's lymphomas: distributions of the major subtypes differ by geographic locations. Non- Hodgkin's Lymphoma Classification Project. Ann Oncol. 1998;9(7):717-720. - PubMed
-
- Vose J, Armitage J, Weisenburger D, International TCLP. International peripheral T-cell and natural killer/T-cell lymphoma study: pathology findings and clinical outcomes. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(25):4124-4130. - PubMed
-
- Mak V, Hamm J, Chhanabhai M, et al. . Survival of patients with peripheral T-cell lymphoma after first relapse or progression: spectrum of disease and rare longterm survivors. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31(16):1970-1976. - PubMed
-
- Hwang WY, Koh LP, Lim ST, et al. . Multicenter study of comparative outcomes of hematopoietic stem cell transplant for peripheral T cell lymphoma and natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma. 2011;52(7):1382-1386. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources