Ringworm in calves: risk factors, improved molecular diagnosis, and therapeutic efficacy of an Aloe vera gel extract
- PMID: 33148275
- PMCID: PMC7640396
- DOI: 10.1186/s12917-020-02616-9
Ringworm in calves: risk factors, improved molecular diagnosis, and therapeutic efficacy of an Aloe vera gel extract
Abstract
Background: Dermatophytosis in calves is a major public and veterinary health concern worldwide because of its zoonotic potential and associated economic losses in cattle farms. However, this condition has lacked adequate attention; thus, to develop effective control measures, we determined ringworm prevalence, risk factors, and the direct-sample nested PCR diagnostic indices compared with the conventional methods of dermatophytes identification. Moreover, the phenolic composition of an Aloe vera gel extract (AGE) and its in vitro and in vivo antidermatophytic activity were evaluated and compared with those of antifungal drugs.
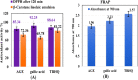
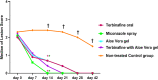
Results: Of the 760 calves examined, 55.79% (424/760) showed ringworm lesions; 84.91% (360/424) were positive for fungal elements in direct-microscopy, and 79.72% (338/424) were positive in culture. Trichophyton verrucosum was the most frequently identified dermatophyte (90.24%). The risk of dermatophytosis was higher in 4-6-month-old vs. 1-month-old calves (60% vs. 41%), and in summer and winter compared with spring and autumn seasons (66 and 54% vs. 48%). Poor hygienic conditions, intensive breeding systems, animal raising for meat production, parasitic infestation, crossbreeding, and newly purchased animals were statistically significant risk factors for dermatophytosis. One-step PCR targeting the conserved regions of the 18S and 28S genes achieved unequivocal identification of T. verrucosum and T. mentagrophytes in hair samples. Nested-PCR exhibited an excellent performance in all tested diagnostic indices and increased the species-specific detection of dermatophytes by 20% compared with culture. Terbinafine and miconazole were the most active antifungal agents for dermatophytes. Gallic acid, caffeic acid, chlorogenic acid, cinnamic acid, aloe-Emodin, quercetin, and rutin were the major phenolic compounds of AGE, as assessed using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). These compounds increased and synergized the antidermatophytic activity of AGE. The treated groups showed significantly lower clinical scores vs. the control group (P < 0.05). The calves were successfully treated with topical AGE (500 ppm), resulting in clinical and mycological cure within 14-28 days of the experiment; however, the recovery was achieved earlier in the topical miconazole 2% and AGE plus oral terbinafine groups.
Conclusions: The nested PCR assay provided a rapid diagnostic tool for dermatophytosis and complemented the conventional methods for initiating targeted treatments for ringworm in calves. The recognized antidermatophytic potential of AGE is an advantageous addition to the therapeutic outcomes of commercial drugs.
Keywords: Aloe vera gel extract; Antifungal drugs; Calves dermatophytosis; Direct-sample nested PCR; Risk factors; Treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors have no competing interests to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
High infection rate of Trichophyton verrucosum in calves from Central Italy.Zoonoses Public Health. 2009 Mar;56(2):59-64. doi: 10.1111/j.1863-2378.2008.01157.x. Epub 2008 Aug 14. Zoonoses Public Health. 2009. PMID: 18705659
-
Assessment of a pan-dermatophyte nested-PCR compared with conventional methods for direct detection and identification of dermatophytosis agents in animals.Mycoses. 2018 Nov;61(11):837-844. doi: 10.1111/myc.12821. Epub 2018 Jul 11. Mycoses. 2018. PMID: 29944743
-
Molecular characterization of dermatophytes isolated from cattle in Plateau State, Nigeria.Vet Microbiol. 2018 Jun;219:212-218. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2018.04.022. Epub 2018 Apr 20. Vet Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29778198
-
Deep facial mycosis due to Trichophyton verrucosum-molecular genetic identification of the dermatophyte in paraffin-embedded tissue-case report and review of the literature.Mycoses. 2018 Mar;61(3):152-158. doi: 10.1111/myc.12719. Epub 2017 Nov 15. Mycoses. 2018. PMID: 29082569 Review.
-
Diagnosis of Dermatophytosis Using Molecular Biology.Mycopathologia. 2017 Feb;182(1-2):193-202. doi: 10.1007/s11046-016-0038-z. Epub 2016 Aug 1. Mycopathologia. 2017. PMID: 27480761 Review.
Cited by
-
Establishment and application of multiplex PCR method for detection of Trichophyton verrucosum, Microsporum canis, and Trichophyton mentagrophytes from cattle.Front Vet Sci. 2025 Mar 24;12:1546586. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1546586. eCollection 2025. Front Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40196810 Free PMC article.
-
Agreement between Clinical Assessment and Laboratory Diagnosis of Ringworm in Calves at Auction Markets.Animals (Basel). 2024 Jan 25;14(3):390. doi: 10.3390/ani14030390. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38338033 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and Risk Factors of Superficial Fungal Infection among Patients Attending a Tertiary Care Hospital in Central Nepal.Interdiscip Perspect Infect Dis. 2022 Oct 4;2022:3088681. doi: 10.1155/2022/3088681. eCollection 2022. Interdiscip Perspect Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 36247346 Free PMC article.
-
Eukaryotic Infections in Dairy Calves: Impacts, Diagnosis, and Strategies for Prevention and Control.Vet Med (Auckl). 2023 Dec 1;14:195-208. doi: 10.2147/VMRR.S442374. eCollection 2023. Vet Med (Auckl). 2023. PMID: 38058381 Free PMC article. Review.
-
First Terbinafine-Resistant Trichophyton indotineae Isolates with Phe397Leu and/or Thr414His Mutations in Turkey.Mycopathologia. 2023 Jan 19;188(1):2. doi: 10.1007/s11046-023-00708-2. Mycopathologia. 2023. PMID: 36656402
References
-
- Shams-Ghahfarokhi M, Mosleh-Tehrani F, Ranjbar-Bahadori S, Razzaghi-Abyaneh M. An epidemiological survey on cattle ringworm in major dairy farms of Mashhad city, Eastern Iran. Iran J Microbiol. 2009;1:31–36.
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

