Multimodal imaging of bacterial-host interface in mice and piglets with Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis
- PMID: 33148623
- PMCID: PMC7818516
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aay2104
Multimodal imaging of bacterial-host interface in mice and piglets with Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis
Abstract
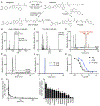
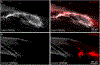
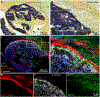
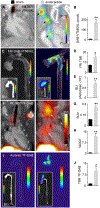
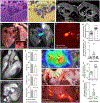
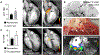
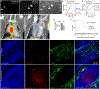
Acute bacterial endocarditis is a rapid, difficult to manage, and frequently lethal disease. Potent antibiotics often cannot efficiently kill Staphylococcus aureus that colonizes the heart's valves. S. aureus relies on virulence factors to evade therapeutics and the host's immune response, usurping the host's clotting system by activating circulating prothrombin with staphylocoagulase and von Willebrand factor-binding protein. An insoluble fibrin barrier then forms around the bacterial colony, shielding the pathogen from immune cell clearance. Targeting virulence factors may provide previously unidentified avenues to better diagnose and treat endocarditis. To tap into this unused therapeutic opportunity, we codeveloped therapeutics and multimodal molecular imaging to probe the host-pathogen interface. We introduced and validated a family of small-molecule optical and positron emission tomography (PET) reporters targeting active thrombin in the fibrin-rich environment of bacterial colonies. The imaging agents, based on the clinical thrombin inhibitor dabigatran, are bound to heart valve vegetations in mice. Using optical imaging, we monitored therapy with antibodies neutralizing staphylocoagulase and von Willebrand factor-binding protein in mice with S. aureus endocarditis. This treatment deactivated bacterial defenses against innate immune cells, decreased in vivo imaging signal, and improved survival. Aortic or tricuspid S. aureus endocarditis in piglets was also successfully imaged with clinical PET/magnetic resonance imaging. Our data map a route toward adjuvant immunotherapy for endocarditis and provide efficient tools to monitor this drug class for infectious diseases.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works.
Figures
References
-
- Cahill TJ, Baddour LM, Habib G, Hoen B, Salaun E, Pettersson GB, Schäfers HJ, Prendergast BD, Challenges in Infective Endocarditis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 69(3),325–344 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Friedrich R, Panizzi P, Fuentes-Prior P, Richter K, Verhamme I, Anderson PJ, Kawabata S, Huber R, Bode W, Bock PE, Staphylocoagulase is a prototype for the mechanism of cofactor-induced zymogen activation. Nature. 425(6957),535–9 (2003). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL144072/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL130018/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL131478/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL131495/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 HL139598/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA220234/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P41 EB017183/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R37 HL071544/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL071544/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA049547/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL114477/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

