Pathogenic, glycolytic PD-1+ B cells accumulate in the hypoxic RA joint
- PMID: 33148884
- PMCID: PMC7710281
- DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.139032
Pathogenic, glycolytic PD-1+ B cells accumulate in the hypoxic RA joint
Abstract
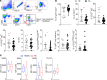
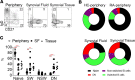
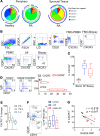
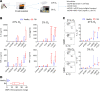
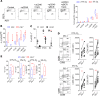
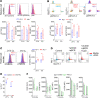
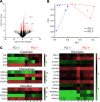
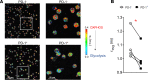
While autoantibodies are used in the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), the function of B cells in the inflamed joint remains elusive. Extensive flow cytometric characterization and SPICE algorithm analyses of single-cell synovial tissue from patients with RA revealed the accumulation of switched and double-negative memory programmed death-1 receptor-expressing (PD-1-expressing) B cells at the site of inflammation. Accumulation of memory B cells was mediated by CXCR3, evident by the observed increase in CXCR3-expressing synovial B cells compared with the periphery, differential regulation by key synovial cytokines, and restricted B cell invasion demonstrated in response to CXCR3 blockade. Notably, under 3% O2 hypoxic conditions that mimic the joint microenvironment, RA B cells maintained marked expression of MMP-9, TNF, and IL-6, with PD-1+ B cells demonstrating higher expression of CXCR3, CD80, CD86, IL-1β, and GM-CSF than their PD-1- counterparts. Finally, following functional analysis and flow cell sorting of RA PD-1+ versus PD-1- B cells, we demonstrate, using RNA-Seq and emerging fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy of cellular NAD, a significant shift in metabolism of RA PD-1+ B cells toward glycolysis, associated with an increased transcriptional signature of key cytokines and chemokines that are strongly implicated in RA pathogenesis. Our data support the targeting of pathogenic PD-1+ B cells in RA as a focused, novel therapeutic option.
Keywords: B cells; Cell Biology; Metabolism; Rheumatology; hypoxia.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
PD-1 Expression on CD8+CD28- T cells within inflammatory synovium is associated with Relapse: A cohort of Rheumatoid Arthritis.Immunol Lett. 2020 Dec;228:76-82. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2020.10.005. Epub 2020 Oct 15. Immunol Lett. 2020. PMID: 33069765
-
Elevated expression of interleukin-7 receptor in inflamed joints mediates interleukin-7-induced immune activation in rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Rheum. 2009 Sep;60(9):2595-605. doi: 10.1002/art.24754. Arthritis Rheum. 2009. PMID: 19714586
-
Role of CXCL13 and CCL20 in the recruitment of B cells to inflammatory foci in chronic arthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2018 Jun 7;20(1):114. doi: 10.1186/s13075-018-1611-2. Arthritis Res Ther. 2018. PMID: 29880013 Free PMC article.
-
Morphological and molecular pathology of the B cell response in synovitis of rheumatoid arthritis.Virchows Arch. 2002 Nov;441(5):415-27. doi: 10.1007/s00428-002-0702-1. Epub 2002 Nov 5. Virchows Arch. 2002. PMID: 12447670 Review.
-
Cellular and molecular perspectives in rheumatoid arthritis.Semin Immunopathol. 2017 Jun;39(4):343-354. doi: 10.1007/s00281-017-0633-1. Epub 2017 May 15. Semin Immunopathol. 2017. PMID: 28508153 Review.
Cited by
-
Unraveling the complex interplay between anti-tumor immune response and autoimmunity mediated by B cells and autoantibodies in the era of anti-checkpoint monoclonal antibody therapies.Front Immunol. 2024 Jan 22;15:1343020. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1343020. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38318190 Free PMC article. Review.
-
2P-FLIM unveils time-dependent metabolic shifts during osteogenic differentiation with a key role of lactate to fuel osteogenesis via glutaminolysis identified.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023 Dec 12;14(1):364. doi: 10.1186/s13287-023-03606-y. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023. PMID: 38087380 Free PMC article.
-
Computational approaches in rheumatic diseases - Deciphering complex spatio-temporal cell interactions.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2023 Aug 6;21:4009-4020. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2023.08.005. eCollection 2023. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2023. PMID: 37649712 Free PMC article. Review.
-
B cell immunometabolism in health and disease.Nat Immunol. 2025 Mar;26(3):366-377. doi: 10.1038/s41590-025-02102-0. Epub 2025 Feb 21. Nat Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39984733 Review.
-
ACPA Status Correlates with Differential Immune Profile in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis.Cells. 2021 Mar 14;10(3):647. doi: 10.3390/cells10030647. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33799480 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

