Introducing Biomedisa as an open-source online platform for biomedical image segmentation
- PMID: 33149150
- PMCID: PMC7642381
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-19303-w
Introducing Biomedisa as an open-source online platform for biomedical image segmentation
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Introducing Biomedisa as an open-source online platform for biomedical image segmentation.Nat Commun. 2024 Oct 23;15(1):9141. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-53245-x. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39443454 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
We present Biomedisa, a free and easy-to-use open-source online platform developed for semi-automatic segmentation of large volumetric images. The segmentation is based on a smart interpolation of sparsely pre-segmented slices taking into account the complete underlying image data. Biomedisa is particularly valuable when little a priori knowledge is available, e.g. for the dense annotation of the training data for a deep neural network. The platform is accessible through a web browser and requires no complex and tedious configuration of software and model parameters, thus addressing the needs of scientists without substantial computational expertise. We demonstrate that Biomedisa can drastically reduce both the time and human effort required to segment large images. It achieves a significant improvement over the conventional approach of densely pre-segmented slices with subsequent morphological interpolation as well as compared to segmentation tools that also consider the underlying image data. Biomedisa can be used for different 3D imaging modalities and various biomedical applications.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

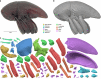

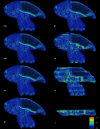


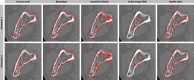
References
-
- Maire, E. & Withers, P. J. Quantitative X-ray tomography. Int. Mater. Rev.59, 1–43 (2014).
-
- Litjens, G. et al. A survey on deep learning in medical image analysis. Med. Image Anal.42, 60–88 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Christ, P. F. et al. Automatic liver and lesion segmentation in CT using cascaded fully convolutional neural networks and 3D conditional random fields. In Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2016 (eds Ourselin, S. et al.) 415–423 (Springer, Cham, 2016).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

