IFITM3 functions as a PIP3 scaffold to amplify PI3K signalling in B cells
- PMID: 33149299
- PMCID: PMC8087162
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-020-2884-6
IFITM3 functions as a PIP3 scaffold to amplify PI3K signalling in B cells
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: IFITM3 functions as a PIP3 scaffold to amplify PI3K signalling in B cells.Nature. 2021 Apr;592(7852):E3. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03388-4. Nature. 2021. PMID: 33712811 No abstract available.
Abstract
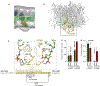
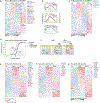
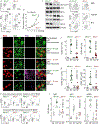
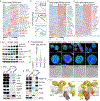
Interferon-induced transmembrane protein 3 (IFITM3) has previously been identified as an endosomal protein that blocks viral infection1-3. Here we studied clinical cohorts of patients with B cell leukaemia and lymphoma, and identified IFITM3 as a strong predictor of poor outcome. In normal resting B cells, IFITM3 was minimally expressed and mainly localized in endosomes. However, engagement of the B cell receptor (BCR) induced both expression of IFITM3 and phosphorylation of this protein at Tyr20, which resulted in the accumulation of IFITM3 at the cell surface. In B cell leukaemia, oncogenic kinases phosphorylate IFITM3 at Tyr20, which causes constitutive localization of this protein at the plasma membrane. In a mouse model, Ifitm3-/- naive B cells developed in normal numbers; however, the formation of germinal centres and the production of antigen-specific antibodies were compromised. Oncogenes that induce the development of leukaemia and lymphoma did not transform Ifitm3-/- B cells. Conversely, the phosphomimetic IFITM3(Y20E) mutant induced oncogenic PI3K signalling and initiated the transformation of premalignant B cells. Mechanistic experiments revealed that IFITM3 functions as a PIP3 scaffold and central amplifier of PI3K signalling. The amplification of PI3K signals depends on IFITM3 using two lysine residues (Lys83 and Lys104) in its conserved intracellular loop as a scaffold for the accumulation of PIP3. In Ifitm3-/- B cells, lipid rafts were depleted of PIP3, which resulted in the defective expression of over 60 lipid-raft-associated surface receptors, and impaired BCR signalling and cellular adhesion. We conclude that the phosphorylation of IFITM3 that occurs after B cells encounter antigen induces a dynamic switch from antiviral effector functions in endosomes to a PI3K amplification loop at the cell surface. IFITM3-dependent amplification of PI3K signalling, which in part acts downstream of the BCR, is critical for the rapid expansion of B cells with high affinity to antigen. In addition, multiple oncogenes depend on IFITM3 to assemble PIP3-dependent signalling complexes and amplify PI3K signalling for malignant transformation.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests
The authors have no competing interests.
Figures




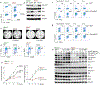
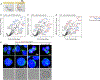
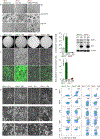
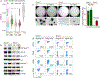


Comment in
-
IFITM3 Enhances PI3K Pathway Signaling to Promote B-cell Malignancies.Cancer Discov. 2021 Jan;11(1):12. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-RW2020-168. Epub 2020 Nov 20. Cancer Discov. 2021. PMID: 33218971
References
-
- Zhang Y, Qin L, Zhao Y, Zhang P, Xu B, Li K, Liang L, Zhang C, Dai Y, Feng Y, Sun J, Hu Z, Xiang H, Knight JC, Dong T, Jin R. Interferon-Induced Transmembrane Protein 3 Genetic Variant rs12252-C Associated with disease severity in Coronavirus Disease 2019. J Infect Dis. 222: 34–37 (2020). - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- AI140718/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA232563/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- AI116585/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- P41 GM108569/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA233412/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM117923/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R35 CA197628/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 CA231958/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI104002/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI140705/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R35 CA200422/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- AI116585S/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI116585/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI127513/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 110275/Z/15/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- R01 CA213138/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM097261/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 LM013876/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI140718/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI140705/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- DE023926/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA157644/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- DE028521/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA060553/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE023926/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA251275/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- S10 OD025194/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA217377/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE028521/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

