Regenerative Capacity of Dental Pulp Stem Cells: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 33149427
- PMCID: PMC7595477
- DOI: 10.4103/jpbs.JPBS_121_20
Regenerative Capacity of Dental Pulp Stem Cells: A Systematic Review
Abstract
Objectives: The dental pulp contains undifferentiated mesenchymal cells, blood vessels and so on, which are responsible for routine functions of a tooth. The determination of stemness and regenerative properties using biomarkers and further application in routine practice may unravel its potential.
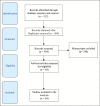
Materials and methods: Inclusion criteria-original research articles published in English, from 2000 to 2019, were collected both manually and by electronic search from databases of Cochrane, Medline, Embase, and PubMed. Exclusion criteria-articles other than English and review manuscripts were omitted. The shortlisted articles were reviewed for specific biomarkers, to assess the regenerative potential, stemness, and lineage of dental pulp stem cells.
Results: Of 512 articles, 64 were selected and reviewed to determine the mesenchymal, neurogenic, vasculogenic, hematopoietic, and stem cell potential. On the basis of the search analysis, a panel of markers was proposed.
Conclusion: The application of proposed markers, on a pulpectomized tissue derived from human teeth, may be helpful to determine the regenerative potential and the usefulness in regenerative medicine and tissue engineering.
Keywords: Biomarkers; dental pulp stem cells; regenerative medicine; stem cells; tissue engineering.
Copyright: © 2020 Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
References
-
- Sloan AJ, Waddington RJ. Dental pulp stem cells: what, where, how? Int J Paediatr Dent. 2009;19:61–70. - PubMed
-
- Apel C, Forlenza OV, de Paula VJ, Talib LL, Denecke B, Eduardo CP, et al. The neuroprotective effect of dental pulp cells in models of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm. 2009;116:71–8. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources