Two-Year Multicenter Outcomes of iStent inject Trabecular Micro-Bypass Stents Combined with Phacoemulsification in Various Types of Glaucoma and Ocular Hypertension
- PMID: 33149544
- PMCID: PMC7604539
- DOI: 10.2147/OPTH.S271646
Two-Year Multicenter Outcomes of iStent inject Trabecular Micro-Bypass Stents Combined with Phacoemulsification in Various Types of Glaucoma and Ocular Hypertension
Abstract
Purpose: This multicenter study evaluated 2-year effectiveness and safety following implantation of two second-generation trabecular micro-bypass stents (iStent inject ®) with phacoemulsification.
Materials and methods: This was a retrospective study of iStent inject implantation with phacoemulsification by nine surgeons across Australia. Eyes had mild to advanced glaucoma (predominantly primary open-angle/POAG, appositional angle-closure/ACG, or normal-tension/NTG) or ocular hypertension (OHT), and cataract. Evaluations included intraocular pressure (IOP); medications; proportions of eyes with 0 or ≥2 medications, reduced/stable medications versus preoperative, and IOP ≤15 mmHg; visual acuity; cup-to-disc ratio (CDR); visual fields (VF); adverse events; and secondary surgery.
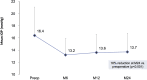
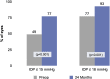
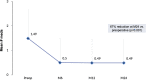
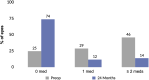
Results: A total of 340 eyes underwent surgery and had 24-month follow-up data. At 24 months, mean IOP decreased by 16% from 16.4±4.7 mmHg preoperatively to 13.7±3.1 mmHg (p<0.001), and 77% of eyes achieved IOP of ≤15 mmHg versus 49% preoperatively (p<0.001). Mean number of medications decreased by 67% to 0.49±0.95 versus 1.49±1.20 preoperatively (p<0.001), with 74% of eyes medication-free versus 25% preoperatively (p<0.001), and 14% of eyes on ≥2 medications versus 46% preoperatively (p<0.001). Medication burden was reduced or stable in 98% of eyes versus preoperative. Stratified analyses showed significant IOP and medication reductions across glaucoma subtypes (POAG, ACG, NTG, OHT): 13-22% for IOP (p<0.01 for all) and 62-100% for medication (p<0.001 for all). Favorable safety included few adverse events; stable CDR, VF, and visual acuity; and filtering surgery in only 8 eyes (2.4%) over 2 years.
Conclusion: This 340-eye multicenter dataset provides robust evidence of the safety and efficacy of iStent inject implantation with phacoemulsification, with significant and sustained IOP and medication reductions through 2 years. Results were similarly favorable across glaucoma subtypes (including POAG, ACG, NTG, OHT) and were attained across various glaucoma severities, clinical sites, and surgeons, highlighting the real-world versatility and utility of this treatment modality.
Keywords: MIGS; glaucoma; iStent inject; intraocular pressure; microinvasive glaucoma surgery; multicenter; second-generation.
© 2020 Clement et al.
Conflict of interest statement
CC reports personal fees from Allergan, Glaukos, Alcon, Merck, Sharp, Dohme. FH reports personal fees from Glaukos. ASI is a consultant for Glaukos. DM reports personal fees from Glaukos, Allergan, and Alcon including being a consultant for Alcon. JL reports research grants from Sydney Eye Hospital Foundation, Glaukos, and Zeiss. RL reports personal fees from Allergan and is a consultant for Glaukos. SS reports honoraria as a consultant from Glaukos. TG reports personal fees from and serves in the advisory board for Glaukos. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

References
-
- Gedde SJ, Herndon LW, Brandt JD, Budenz DL, Feuer WJ, Schiffman JC; Tube Versus Trabeculectomy Study Group. Postoperative complications in the Tube Versus Trabeculectomy (TVT) study during five years of follow-up. Am J Ophthalmol. 2012;153:804–814. doi: 10.1016/j.ajo.2011.10.024 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

