Targeting Yes1 Associated Transcriptional Regulator Inhibits Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression and Improves Sensitivity to Sorafenib: An in vitro and in vivo Study
- PMID: 33149619
- PMCID: PMC7605682
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S249412
Targeting Yes1 Associated Transcriptional Regulator Inhibits Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression and Improves Sensitivity to Sorafenib: An in vitro and in vivo Study
Abstract
Purpose: The aim of this study was to investigate the role of Yes1 associated transcriptional regulator (YAP1) in the pathology of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and its potential as a therapeutic target.
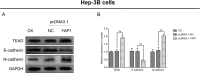
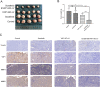
Methods: YAP1 expression in HCC and adjacent tissues was determined via immunohistochemistry; in HCC and human normal liver cell lines, expression was examined via Western blotting. The effects of YAP1 knockdown and overexpression were detected following transfection of HCC cells with siRNA-YAP1 recombinants or pcDNA3.1-YAP1 plasmids. A tumor xenograft model was constructed by implanting YAP1-knockdown lentivirus-infected Hep-3B cells into nude mice, and the animals were treated with sorafenib.
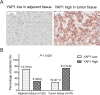
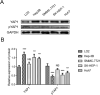
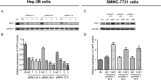
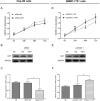
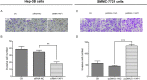
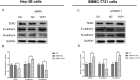
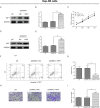
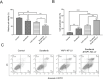
Results: In patients with HCC, YAP1 was upregulated in tumor tissue compared with adjacent tissue, and its high expression in the tumor was associated with increased Edmonson grade. In vitro, YAP1 expression was increased in Hep-3B, SK-HEP-1 and Huh7 cells, while it was similar in SMMC-7721 cells and LO2 cells. Meanwhile, YAP1 increased cell proliferation and invasion, promoted the progression of epithelial-mesenchymal transition, and inhibited cell apoptosis in HCC cells; furthermore, YAP1 knockdown combined with the administration of sorafenib decreased cell viability and increased cell apoptosis compared with YAP1 knockdown or treatment with sorafenib alone. In vivo, YAP1 knockdown inhibited tumor growth and metastasis, whereas it promoted apoptosis; meanwhile, YAP1 knockdown synergized with sorafenib to suppress tumor progression in HCC mice.
Conclusion: YAP1 is upregulated in both HCC tumor tissues and cell lines. Moreover, it promotes cell proliferation and invasion and promoted the progression of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in vitro. Furthermore, targeting YAP1 inhibits HCC progression and improves sensitivity to sorafenib in vitro and in vivo.
Keywords: Yes1 associated transcriptional regulator; apoptosis; hepatocellular carcinoma; invasion; proliferation; sorafenib.
© 2020 Guo et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work. Liwen Guo and Jiaping Zheng are co-first authors for this study.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[YAP regulates the proliferation and modifies the sensitivity to sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma cells].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2018 Nov 23;40(11):818-823. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3766.2018.11.004. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 30481931 Chinese.
-
Increased expression of SLC46A3 to oppose the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma and its effect on sorafenib therapy.Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Jun;114:108864. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.108864. Epub 2019 Apr 10. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 30981107
-
MEX3A determines in vivo hepatocellular carcinoma progression and induces resistance to sorafenib in a Hippo-dependent way.Hepatol Int. 2023 Dec;17(6):1500-1518. doi: 10.1007/s12072-023-10565-2. Epub 2023 Jul 17. Hepatol Int. 2023. PMID: 37460832
-
SIX4 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis through upregulating YAP1 and c-MET.Oncogene. 2020 Dec;39(50):7279-7295. doi: 10.1038/s41388-020-01500-y. Epub 2020 Oct 12. Oncogene. 2020. PMID: 33046796
-
Downregulation of CENPK suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma malignant progression through regulating YAP1.Onco Targets Ther. 2019 Jan 29;12:869-882. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S190061. eCollection 2019. Onco Targets Ther. 2019. PMID: 30774374 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Cancer Cell-Intrinsic Alterations Associated with an Immunosuppressive Tumor Microenvironment and Resistance to Immunotherapy in Lung Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jun 6;15(12):3076. doi: 10.3390/cancers15123076. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37370686 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Small Interfering RNAs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.J Gastrointest Cancer. 2024 Mar;55(1):26-40. doi: 10.1007/s12029-023-00911-w. Epub 2023 Jul 11. J Gastrointest Cancer. 2024. PMID: 37432548 Review.
-
Transcription factor glucocorticoid modulatory element-binding protein 1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by activating Yes-associate protein 1.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2023 Jun 15;15(6):988-1004. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v15.i6.988. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37389116 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Heimbach JK, Kulik LM, Finn RS, et al. AASLD guidelines for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2018;67(1):358–380. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

