Association Between FeNO, Total Blood IgE, Peripheral Blood Eosinophil and Inflammatory Cytokines in Partly Controlled Asthma
- PMID: 33149625
- PMCID: PMC7605921
- DOI: 10.2147/JAA.S274022
Association Between FeNO, Total Blood IgE, Peripheral Blood Eosinophil and Inflammatory Cytokines in Partly Controlled Asthma
Abstract
Background: Fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FeNO) is a convenient to use biomarker of airway inflammation. However, the mutual relationship between FeNO, peripheral blood eosinophil, total immunoglobulin E (IgE) and inflammatory cytokines showed some controversy.
Objective: This study was carried out to determine the accuracy of peripheral blood eosinophil and total IgE to detect eosinophilic airway inflammation as determined by two FeNO cutoff points. The correlation between FeNO, peripheral blood eosinophil, total IgE and certain inflammatory cytokines was also examined.
Methods: Seventy-six patients with partly controlled asthma performed the following tests on the same day: FeNO, pulmonary function tests (PFTs), peripheral blood eosinophils, total IgE, and inflammatory cytokine assay. The correlation between these markers was investigated and the diagnostic accuracy of peripheral blood eosinophils and total IgE to identify eosinophilic asthma phenotype was calculated using receiver operating characteristics area under the curve (ROC AUC).
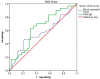
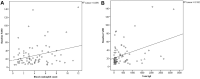
Results: FeNO was positively correlated with percentage of blood eosinophils (r=0.276, p=0.017) and total blood IgE (r=0.3647; p=0.0013). No relationship between FeNO and serum inflammatory cytokines was detected. AUC of blood eosinophils and total IgE were 57% and 64% at FeNO ≥25 ppb and were 67% and 64% at FeNO >50, respectively. The higher predictive ability was detected at FeNO >50 ppb where the best cutoff point for blood eosinophil % was ≥4.0% (sensitivity 66.7%, specificity 60.0%) and the best cutoff point for total IgE was ≥350 (sensitivity 66.7%, specificity 63.6%).
Conclusion: In patients with partly controlled asthma, peripheral blood eosinophil and total IgE showed equal useful accuracy in predicting eosinophilic airways. However, higher predictive values were reported at FeNO level >50 ppb. FeNO was positively correlated with peripheral blood eosinophil, total IgE but not with any of the studied cytokines.
Keywords: FeNO; IgE; cytokines; eosinophils; partly controlled asthma.
© 2020 Badar et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Correlation Between Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide (FeNO), Blood Eosinophil Count, Immunoglobulin E Levels, and Spirometric Values in Patients With Asthma.Cureus. 2023 Feb 22;15(2):e35289. doi: 10.7759/cureus.35289. eCollection 2023 Feb. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 36968856 Free PMC article.
-
Association between fractional exhaled nitric oxide, sputum induction and peripheral blood eosinophil in uncontrolled asthma.Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2018 May 23;14:21. doi: 10.1186/s13223-018-0248-7. eCollection 2018. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29796021 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between total serum immunoglobulin E levels, fractional exhaled breath nitric oxide levels and absolute blood eosinophil counts in atopic and non-atopic asthma: a controlled comparative study.J Breath Res. 2018 Feb 20;12(2):026009. doi: 10.1088/1752-7163/aa95da. J Breath Res. 2018. PMID: 29068321 Clinical Trial.
-
Low-grade disease activity in early life precedes childhood asthma and allergy.Dan Med J. 2016 Aug;63(8):B5272. Dan Med J. 2016. PMID: 27477800 Review.
-
What is the added value of FeNO as T2 biomarker?Front Allergy. 2022 Aug 11;3:957106. doi: 10.3389/falgy.2022.957106. eCollection 2022. Front Allergy. 2022. PMID: 36032508 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Association of Nasal and Blood Eosinophils with Serum IgE Level in Allergic Rhinitis and Asthma: A Case-Control Study.Health Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 7;7(11):e70191. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.70191. eCollection 2024 Nov. Health Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39512245 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Nasal Cytology and Serum Atopic Biomarkers in Paediatric Rhinitis.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Feb 2;13(3):555. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13030555. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36766659 Free PMC article.
-
Application of fractional exhaled nitric oxide and nasal nitric oxide in control evaluation of bronchial asthma and diagnosis of allergic rhinitis in children.Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2022 Jan 15;24(1):90-95. doi: 10.7499/j.issn.1008-8830.2108091. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35177182 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
-
Relationship between fraction of exhaled nitric oxide and peripheral eosinophilia in asthma.Ann Med. 2024 Dec;56(1):2382377. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2024.2382377. Epub 2024 Jul 25. Ann Med. 2024. PMID: 39051101 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammatory and pulmonary function characteristics of bronchial asthma induced by COVID‑19 infection.Biomed Rep. 2025 Apr 22;22(6):101. doi: 10.3892/br.2025.1979. eCollection 2025 Jun. Biomed Rep. 2025. PMID: 40322552 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA). Global strategy for asthma management and prevention. 2020. [cited 2020 23 June]; Available from: https://ginasthma.org/gina-reports/. Accessed October10, 2020.
-
- Heffler E, Carpagnano GE, Favero E, et al. Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide (FENO) in the management of asthma: a position paper of the Italian Respiratory Society (SIP/IRS) and Italian Society of Allergy, Asthma and Clinical Immunology (SIAAIC). Multidiscip Respir Med. 2020;15(1):28. doi:10.4081/mrm.2020.36 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

