Burnout in Healthcare Workers: Prevalence, Impact and Preventative Strategies
- PMID: 33149664
- PMCID: PMC7604257
- DOI: 10.2147/LRA.S240564
Burnout in Healthcare Workers: Prevalence, Impact and Preventative Strategies
Abstract
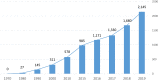
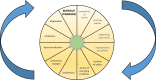
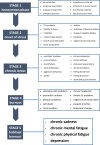
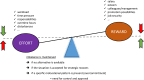
Approximately, one in three physicians is experiencing burnout at any given time. This may not only interfere with own wellbeing but also with the quality of delivered care. This narrative review discusses several aspects of the burnout syndrome: prevalence, symptoms, etiopathogenesis, diagnosis, impact, and strategies on how to deal with the problem.
Keywords: burnout; healthcare worker; impact; prevalence; prevention; symptoms.
© 2020 De Hert.
Conflict of interest statement
The author reports no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures



References
-
- Freudenberger HJ. The staff burn-out syndrome in alternative institutions. Psychotherapy. 1975;12:73–82.
-
- Freudenberger HJ. Burn-out: occupational hazard of the child care worker. Child Care Q. 1977;6:90–99. doi: 10.1007/BF01554695 - DOI
-
- Maslach C, Jackson S. The measurement of experienced burnout. J Occup Behav. 1981;2:99–113. doi: 10.1002/job.4030020205 - DOI
-
- Leiter MP, Schaufeli WB. Consistency of the burnout construct across occupations. Anxiety Stress Coping. 1996;9:229–243. doi: 10.1080/10615809608249404 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

