In-depth transcriptome reveals the potential biotechnological application of Bothrops jararaca venom gland
- PMID: 33149734
- PMCID: PMC7579844
- DOI: 10.1590/1678-9199-JVATITD-2019-0058
In-depth transcriptome reveals the potential biotechnological application of Bothrops jararaca venom gland
Abstract
Background: Lack of complete genomic data of Bothrops jararaca impedes molecular biology research focusing on biotechnological applications of venom gland components. Identification of full-length coding regions of genes is crucial for the correct molecular cloning design.
Methods: RNA was extracted from the venom gland of one adult female specimen of Bothrops jararaca. Deep sequencing of the mRNA library was performed using Illumina NextSeq 500 platform. De novo assembly of B. jararaca transcriptome was done using Trinity. Annotation was performed using Blast2GO. All predicted proteins after clustering step were blasted against non-redundant protein database of NCBI using BLASTP. Metabolic pathways present in the transcriptome were annotated using the KAAS-KEGG Automatic Annotation Server. Toxins were identified in the B. jararaca predicted proteome using BLASTP against all protein sequences obtained from Animal Toxin Annotation Project from Uniprot KB/Swiss-Pro database. Figures and data visualization were performed using ggplot2 package in R language environment.
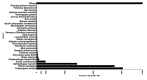
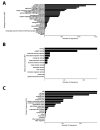
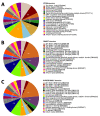
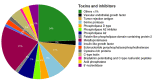
Results: We described the in-depth transcriptome analysis of B. jararaca venom gland, in which 76,765 de novo assembled isoforms, 96,044 transcribed genes and 41,196 unique proteins were identified. The most abundant transcript was the zinc metalloproteinase-disintegrin-like jararhagin. Moreover, we identified 78 distinct functional classes of proteins, including toxins, inhibitors and tumor suppressors. Other venom proteins identified were the hemolytic lethal factors stonustoxin and verrucotoxin.
Conclusion: It is believed that the application of deep sequencing to the analysis of snake venom transcriptomes may represent invaluable insight on their biotechnological potential focusing on candidate molecules.
Keywords: Biotechnological application; Bothrops jararaca; Stonustoxin; Transcriptome; Venom gland; Verrucotoxin.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no potential competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Exploring the Venom Gland Transcriptome of Bothrops asper and Bothrops jararaca: De Novo Assembly and Analysis of Novel Toxic Proteins.Toxins (Basel). 2024 Nov 27;16(12):511. doi: 10.3390/toxins16120511. Toxins (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39728769 Free PMC article.
-
A transcriptomic view of the proteome variability of newborn and adult Bothrops jararaca snake venoms.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2012;6(3):e1554. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0001554. Epub 2012 Mar 13. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2012. PMID: 22428077 Free PMC article.
-
Combined venomics, venom gland transcriptomics, bioactivities, and antivenomics of two Bothrops jararaca populations from geographic isolated regions within the Brazilian Atlantic rainforest.J Proteomics. 2016 Mar 1;135:73-89. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2015.04.029. Epub 2015 May 9. J Proteomics. 2016. PMID: 25968638
-
Jararhagin, a hemorrhagic snake venom metalloproteinase from Bothrops jararaca.Toxicon. 2012 Sep 1;60(3):280-9. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2012.03.026. Epub 2012 Apr 14. Toxicon. 2012. PMID: 22534074 Review.
-
The Bradykinin-potentiating peptides from venom gland and brain of Bothrops jararaca contain highly site specific inhibitors of the somatic angiotensin-converting enzyme.Toxicon. 2005 Jun 15;45(8):1163-70. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2005.02.017. Toxicon. 2005. PMID: 15922781 Review.
Cited by
-
Altered RNome expression in Murine Gastrocnemius Muscle following Exposure to Jararhagin, a Metalloproteinase from Bothrops jararaca Venom.Toxins (Basel). 2022 Jul 9;14(7):472. doi: 10.3390/toxins14070472. Toxins (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35878210 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Venom Gland Transcriptome of Bothrops asper and Bothrops jararaca: De Novo Assembly and Analysis of Novel Toxic Proteins.Toxins (Basel). 2024 Nov 27;16(12):511. doi: 10.3390/toxins16120511. Toxins (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39728769 Free PMC article.
-
Current Technologies in Snake Venom Analysis and Applications.Toxins (Basel). 2024 Oct 25;16(11):458. doi: 10.3390/toxins16110458. Toxins (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39591213 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Computational Modeling of Low-Abundance Proteins in Venom Gland Transcriptomes: Bothrops asper and Bothrops jararaca.Toxins (Basel). 2025 May 22;17(6):262. doi: 10.3390/toxins17060262. Toxins (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40559840 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk of Inflammation and Coagulation in Bothrops Snakebite Envenoming: Endogenous Signaling Pathways and Pathophysiology.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 15;24(14):11508. doi: 10.3390/ijms241411508. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37511277 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
